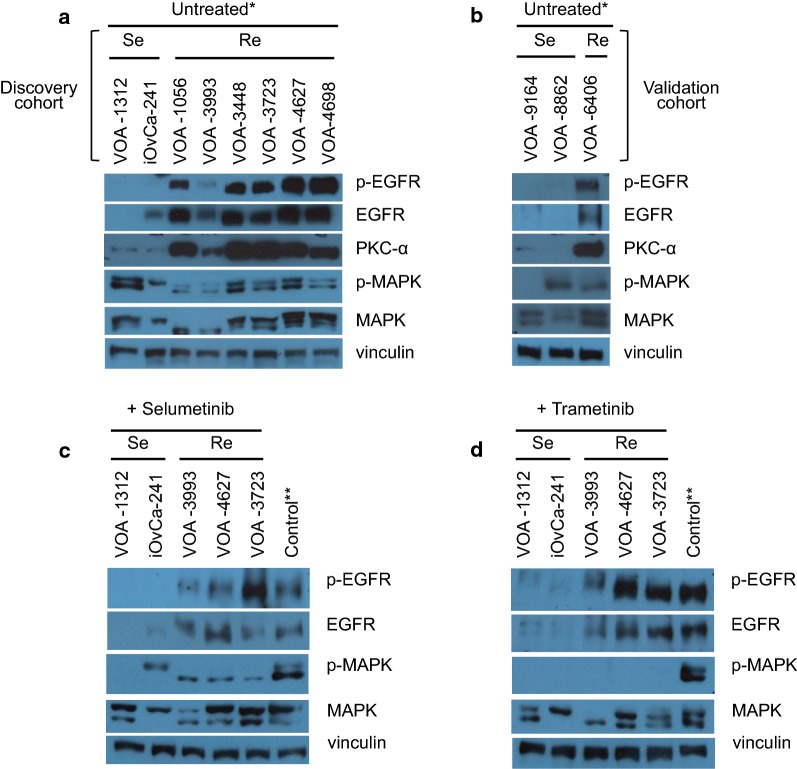
Fig. 2.
Differential expression of EGFR, p-EGFR and PKC-α between MEKi-Se and MEKi-Re LGSC cell lines by WB. a Confirmation of the RPPA results in untreated MEKi-Se and MEKi-Re lines (a, discovery cohort). EGFR, p-EGFR and PKC-α were increased in MEKi-Re lines (n = 5) compared to MEKi-Se lines (n = 2). b Validation of these protein biomarkers in three newly established LGSC cell lines classified according to their MEKi responsiveness (validation cohort). As found in the cell lines analyzed by RPPA, the new MEKi-Re line (n = 1) expressed higher levels of EGFR, p-EGFR and PKC-α compared to the two new MEKi-Se lines tested (n = 2). c, d Confirmation of RPPA results in MEKi treated cell lines. With MEKi treatment (selumetinib 1 μM and trametinib 0.1 μM) p-EGFR expression remained higher in MEKi-Re lines. As previously described, trametinib showed stronger inhibitory effects on MAPK (p-MAPK or p-ERK1/2) than selumetinib, even when used at ten times lower dose. (*) No DMSO. (**) Untreated VOA-4627 cells to control for drug inhibition effects on MAPK pathway