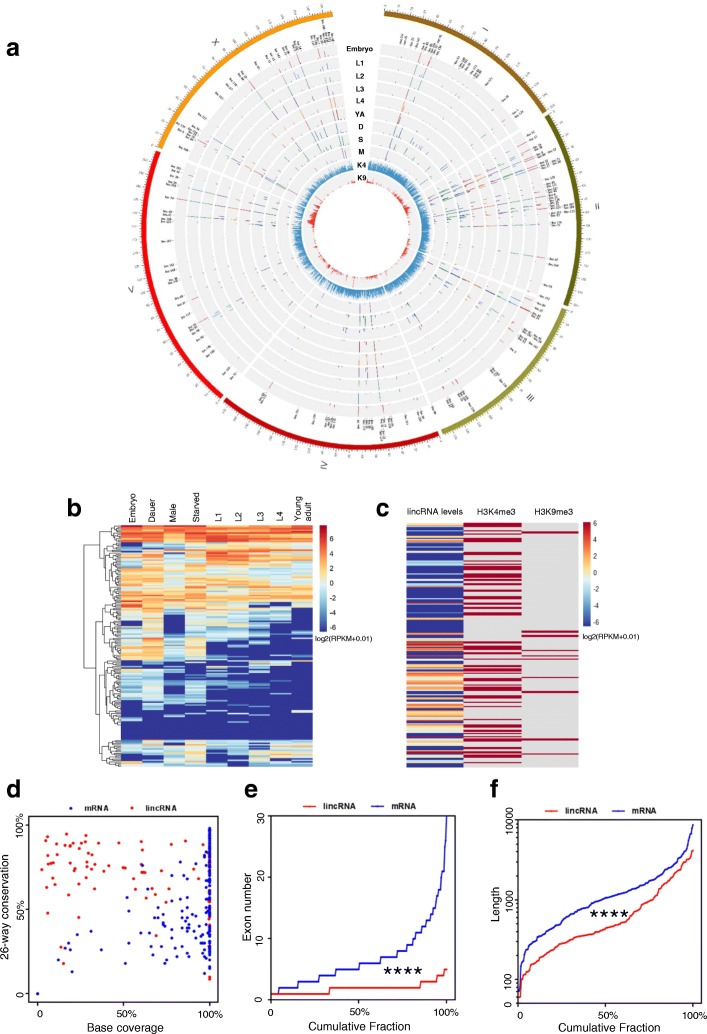
Fig. 1.
Genomic characterization of C. elegans lincRNAs. a Circos plot of the 170 lincRNAs in the C. elegans genome. The expression levels of 170 lincRNAs in nine developmental stages and populations: embryo, L1, L2, L3, and L4, YA (young adult), D (dauer), S (mixed stages of worms under starvation), and M (male, him-5 mix worms) are shown in the inner tracks. The two innermost tracks represent distributions of H3K4me3 (K4) and H3K9me3 (K9) ChIP-seq signals (L4 worms), at the whole genome (not just for lincRNA genes). b Hierarchical clustering of the relative expression levels of the 170 lincRNAs. RNA-seq data from 9 developmental stages were normalized to log2 (RPKM+ 0.01). c lincRNA expression levels (heatmap of RPKM) along with H3K4me3 and H3K9me3 binding (binary map with binding in red) on lincRNA genes. d Conservation score of lincRNAs and mRNAs (n = 200, randomly chosen). “Base coverage” refers to the percentage of annotated bases. Conservation phastCons scores of 26 nematodes were interrogated from the UCSC genome browser [61], and the degree of conservation along with the portion of conserved sequences to the full-length (base coverage) lincRNAs and mRNAs were compared. e Cumulative plot of exon numbers of randomly selected lincRNAs and mRNAs (n = 200, randomly chosen). f Length distribution of lincRNAs and mRNAs (n = 200, randomly chosen). For the analysis of sequence conservation, 26 nematode conservation phastCons scores were interrogated from UCSC [61] for each base of an individual C. elegans lincRNA or mRNA, and the scores of each transcript were averaged. For d and e, ****, p < 0.0001 by the two-sided Mann-Whitney U test