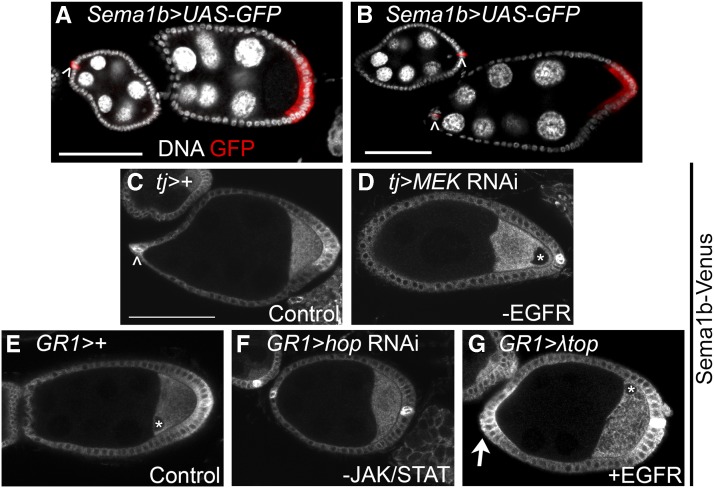
Figure 3.
Sema1b RNA and protein are enriched in the PFCs and polar FCs. Sema1b protein accumulates in FCs with both JAK/STAT and EGFR signaling. A,B) To visualize Sema1b expression during oogenesis, Sema1b-GAL4 was used to drive a UASp-eGFP reporter. Sema1b was observed in the polar follicle cells (arrowheads) and in the PFCs beginning at stage 7 (red). Polar cells outside of this z-plane also express the reporter. C,E) Sema1b-Venus protein trap was used as a reporter for Sema1b protein localization during oogenesis. Sema1b-Venus was detected in the polar follicle cells (arrowhead) and PFCs. Stage 8 is pictured in panels C-E. C) Control (GAL4 only) for comparison to D. D) When MEK RNAi knockdown was very effective in disrupting PFC differentiation, as evidenced by the loss of oocyte nuclear migration (*), Sema1b-Venus enrichment in the PFCs was also disrupted. E) Control (GAL4 only) for comparison to F and G. F) Disruption of JAK/STAT signaling using hop knockdown disrupts Sema1b-Venus accumulation in the PFCs. G) Ectopic expression of constitutively active EGFR (λtop) produces ectopic Sema1b-Venus accumulation in the AFCs (arrow) and occasionally causes a loss of Sema1b enrichment in the PFCs (data not shown). Asterisks (*) mark visible oocyte nuclei. Scale bars represent 50 μm. Table S1 includes quantification of Sema1b-Venus accumulation in the AFC and PFCs and oocyte nuclear migration defects to accompany panels C-G. An anti-GFP antibody was used to detect UAS-GFP in panels A&B and Sema1b-Venus in panels C-G.