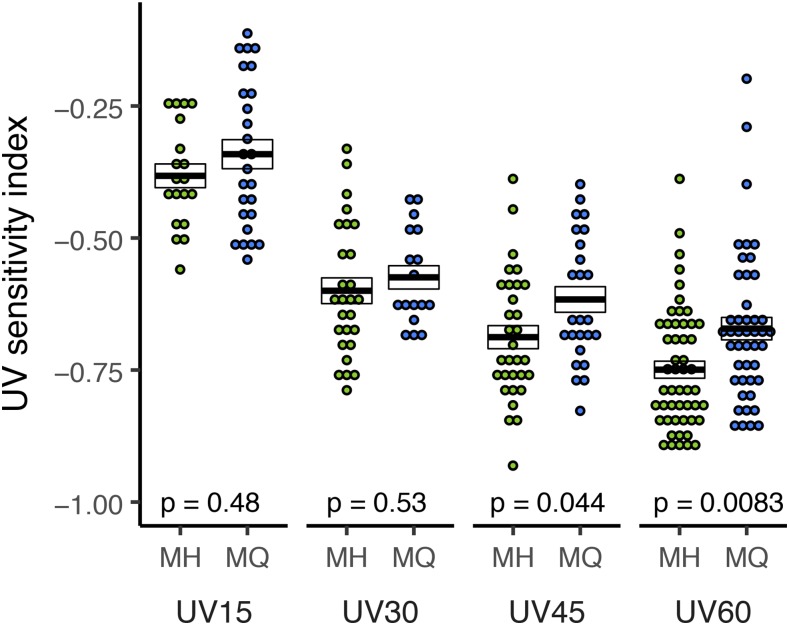
Figure 3.
Early embryo UV sensitivity: The full model ANOVA with Genotype and UV treatment as factors was statistically significant (df = 7, 233; F = 32.62; P < 0.001). Mnn1 (H703Q) contributes to variation in UV sensitivity as the Genotype factor was significant (df = 1; F = 7.90; P = 0.005). UV exposure also had a significant effect (df = 3; F = 68.60; P < 0.001); the interaction was not significant. UV sensitivity index (corresponding to the reduction in embryo hatch rate due to UV exposure) was measured for 1-3 hr. old embryos carrying either of the two Mnn1 alleles. Embryos were exposed to UVB for 15, 30, 45, and 60 sec. Each data point represents the UV sensitivity index of a pool of 25 to 40 embryos. Sample size range is 17 ≤ n ≤ 51 embryo sets. Crossbars represent mean ± SE and p-values correspond to a Wilcoxon test on MH vs. MQ for each UV treatment. UV15: W = 363.5; P = 0.482; UV30 W = 256; P = 0.530; UV45 W = 510; P = 0.044 UV60 W = 1507; P = 0.008. At the 60 sec dose the H allele reduces UV sensitivity by about 12%.