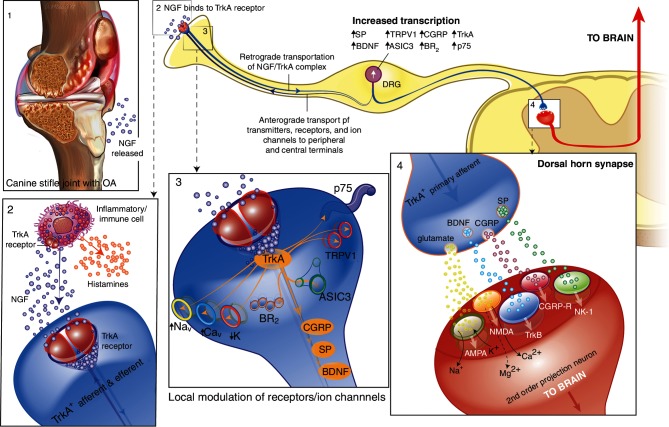
Figure 2.
Schematic diagram of the involvement of nerve growth factor (NGF) in nociception and nervous system plasticity. In osteoarthritis (box 1), NGF is produced and released by peripheral tissues (such as chondrocytes) and can bind to its receptor, TrkA located on primary afferent (sensory) fibres. In addition, NGF that is released in the periphery also binds to TrkA located on mast cells and other immune cells and subsequently elicits the release of inflammatory mediators such as histamine, serotonin (5HT) and NGF itself (box 2). When NGF binds to TrkA, on TrkA-positive primary afferent nerve fibres, the NGF/TrkA complex is internalised and retrogradely transported to the cell body of the sensory neurons that are located in the DRG. This modulates and/or increases the expression of a variety of cell surface receptors and ion channels involved in nociception including TRPV1, ASIC, BR2, Nav, Cav, K and putative mechanotransducers, which result in an increase the excitability of primary afferent fibres (peripheral sensitisation) (box 3). NGF/TrkA signalling also leads to transcriptional changes that result in the increased expression of pronociceptive neurotransmitters such as SP, CGRP and BDNF. When these peptidergic (TrkA-positive) primary afferent neurons are subsequently stimulated, release of these peptides, in addition to glutamate acting on AMPA receptors, and binding to their respective receptors (SP to NK-1, CGRP to CGRP-R, BDNF to TrkB) may cause strong depolarisation of the postsynaptic second order projection neuron (box 4). This will result in the removal of the magnesium (Mg2+) block of the NMDA receptor, facilitating cellular windup. This increases the probability of central sensitisation and facilitated transmission through the dorsal horn synapse and then, via third-order neurons, to the sensory cortex in the brain. Thus, NGF is involved in the processes of inflammation in the periphery, and also in the sensitisation of primary afferent neurons through alteration of their functional phenotype. 5-HT, 5-hydroxytryptamine; AMPA, the α-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazolepropionic acid; ASIC, acid-sensing ion channel; BDNF, brain-derived neurotrophic factor; BR2, bradykinin receptor 2; Cav, voltage-gated calcium channel; CGRP, calcitonin gene-related peptide; CGRP-R, calcitonin gene-related peptide receptor; DRG, dorsal root ganglia; K, delayed-rectifier potassium channel; Nav, voltage-gated sodium channel; NMDA; the glutamatergic N-methyl-D-aspartate; NGF, nerve growth factor; NK-1, neurokinin 1 receptor; p75, neurotrophin receptor; SP, substance P; trkA, tropomyosin receptor kinase A; trkB, tropomyosin receptor kinase B; TRPV1, transient receptor potential vanilloid 1.