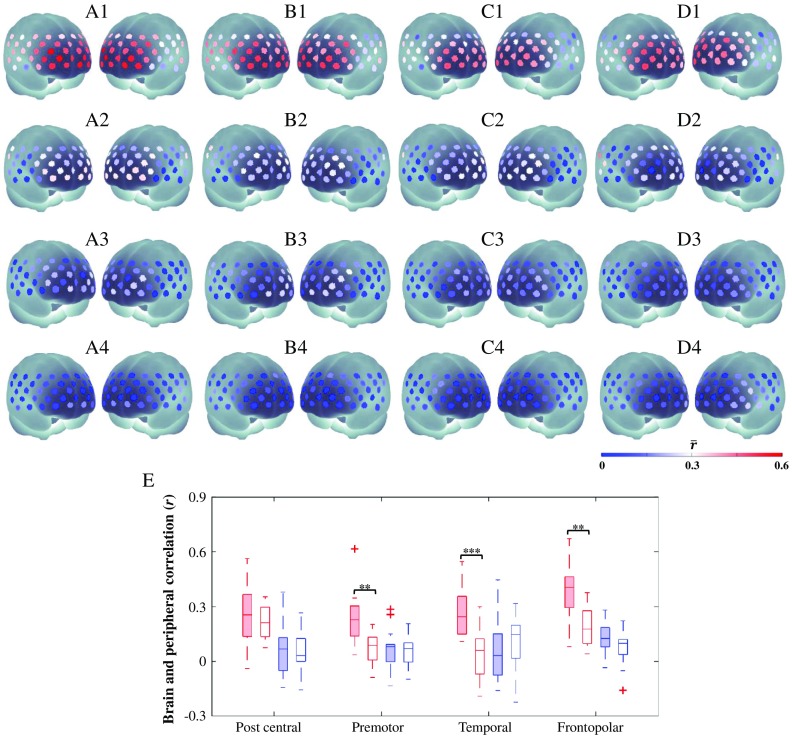
Fig. 7.
Subject-average (A1–D2) and HHb (A3–D4) correlation maps (; inverse -transform) of prefrontal and peripheral signals measured from ears (A1–D1, A3–D3) and finger (A2–D2, A4–D4) during spatial WM (A1–4), motor control (B1–4), eyes-open (C1–4), and eyes-closed RS (D1–4). correlation variances across subjects (E) showing significant differences of peripheral sources (red-filled and red-void boxplots for ear and finger signals, respectively) in premotor, temporal, and prefrontal cortices – (***), (**) for paired-sample -test. There was no observed effect of peripheral sources in HHb correlations of all regions (blue-filled and blue-void boxplots for ear and finger signals, respectively).