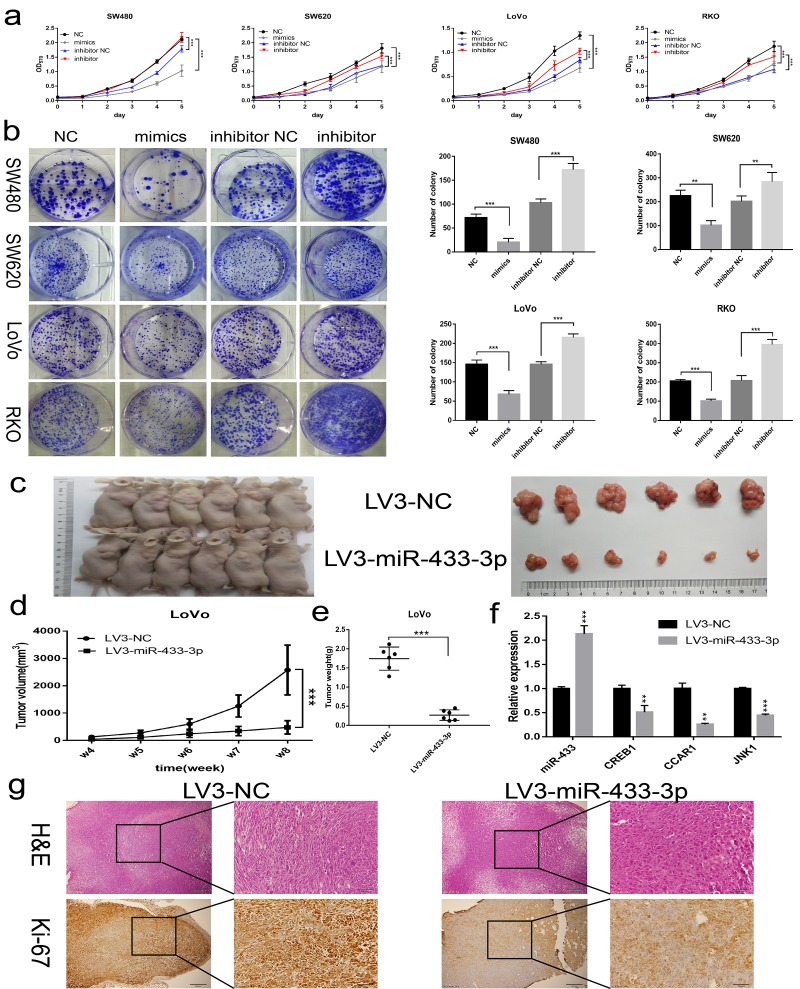
Figure 2.
miR-433 inhibited CRC cell proliferation in vitro and in vivo. (a) MTT assays revealed that transfection of miR-433 mimics evidently suppressed the cell viability in SW480, SW620, LoVo and RKO cells, however, miR-433 inhibitor conspicuously enhanced the proliferative activity relative to inhibitor NC (NC, negative control; mimics, miR-433 mimics; inhibitor NC, negative control for inhibitor; inhibitor, inhibitor of miR-433). (b) Colony formation assays indicated that overexpression or knockdown of miR-433 prominently impeded or promoted CRC cell colony formation activity via transfection of the mimics or inhibitor of miR-433 (NC, negative control; mimics, miR-433 mimics; inhibitor NC, negative control for inhibitor; inhibitor, inhibitor of miR-433). (c) Subcutaneous tumors generated in nude mice which derived from LV3-NC- and LV3-miR-433-3p-infected LoVo cells are shown. (d) ANOVA of repeated measurements confirmed that the LoVo/LV3-miR-433-3p group showed much feebler growth than its counterpart. (e) A t test demonstrated a significant difference in tumor weight between the LoVo/LV3-miR-433-3p group and its counterpart. (f) Real-time PCR indicated that miR-433 was upregulated in LoVo/LV3-miR-433-3p tumors, and subsequently, a dramatic decline in CREB1, CCAR1 and JNK1 was observed. (g) H&E and Ki-67 staining of tumors initiated from LoVo/LV3-NC and LoVo/LV3-miR-433-3p cells. **, p<0.01; ***, p<0.001.