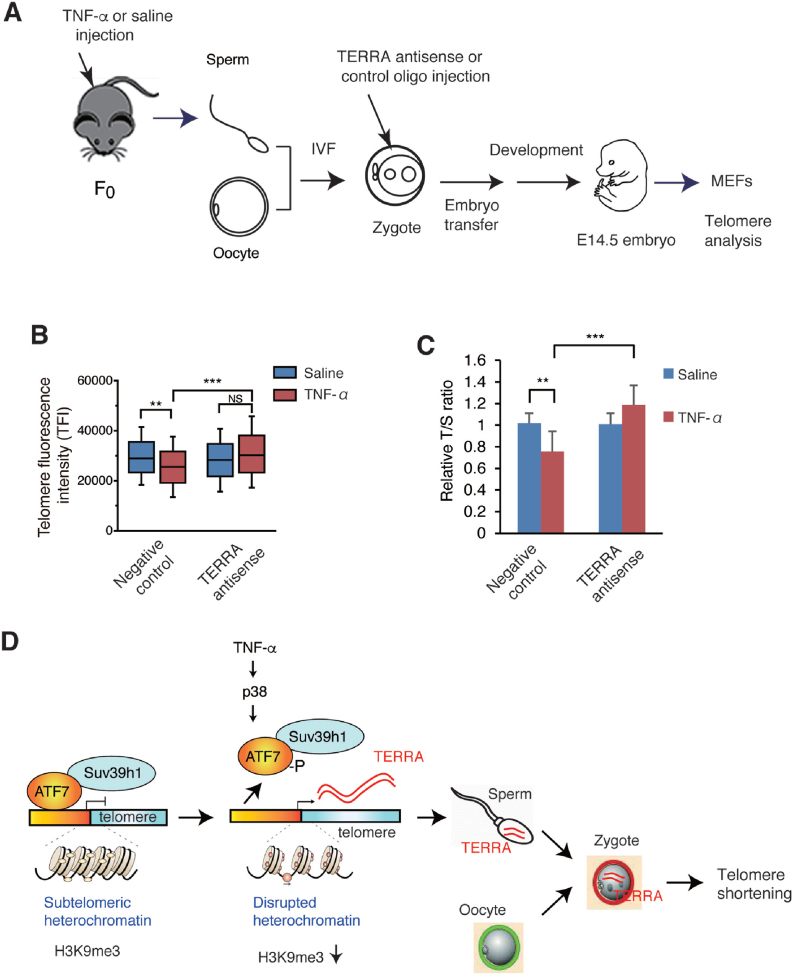
Figure 7.
Injection of TERRA antisense LNA-oligonucleotide into zygotes blocked paternal TNF-α-induced telomere shortening. (A) Scheme of experimental procedures. WT male F0 mice (n = 2) were administered with TNF-α or saline as described in Figure 1A. Spermatozoa were collected for IVF, and the zygote was injected with TERRA antisense or control LNA-oligonucleotides. Zygotes were then transferred into the oviducts of pseudopregnant females, and MEFs were prepared from E14.5 male embryos. (B, C) Telomere length in MEFs was measured by Q-FISH (B) or Q-PCR (C). Three independent male MEFs from two independent pregnant mice were used for Q-FISH. Raw data of Q-FISH are shown in Supplementary Figure S7D. 7, 5, 13 and 13 for each type of MEFs from two independent pregnant mice were used for Q-PCR. **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001; NS, not significant. (D) Model for paternal TNF-α-induced telomere shortening in offspring. In testicular germ cells, ATF7 silences TERRA gene transcription by forming heterochromatin structure on the TERRA gene promoter in the subtelomeric region via recruiting histone H3K9 trimethyltransferase, Suv39h1. TNF-α exposure induces ATF7 phosphorylation by p38, which causes a release of ATF7 from the TERRA gene promoter, resulting to disruption of heterochromatin structure and induction of TERRA gene transcription. TERRA is transgenerationally transmitted to zygotes via sperm, and induces telomere shortening in the male offspring.