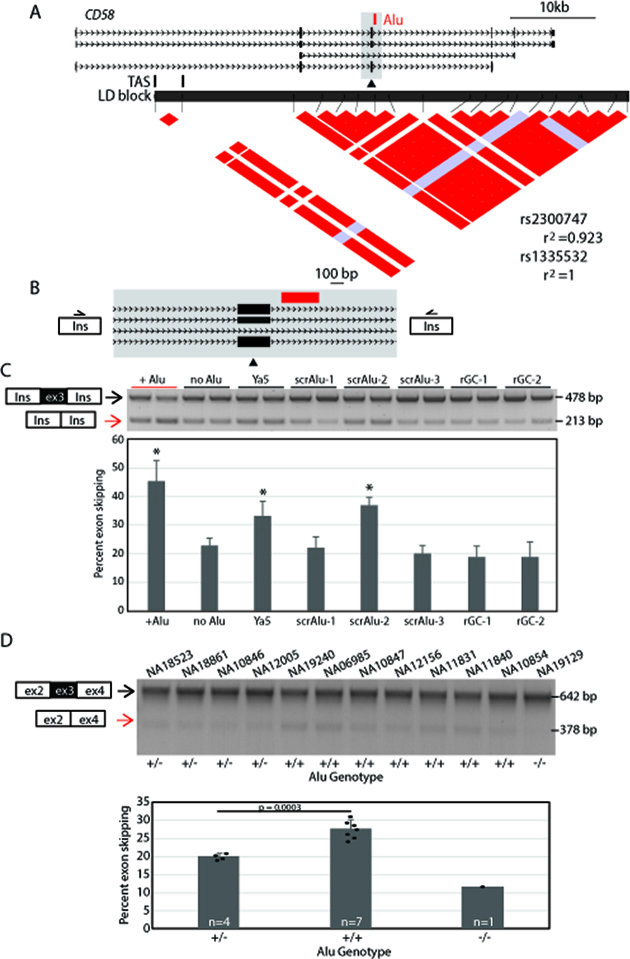
Figure 5.
An Alu variant associated with MS risk is an sQTL at CD58. A) CD58 locus. Trait associated SNPs (TAS, vertical black lines) identify this as a multiple sclerosis risk locus by GWAS. The LD structure from the GWAS identified LD block (black horizontal line) was generated by pair-wise comparisons of variants. Two variants in near perfect LD (r2 > 0.9) are depicted with red coloring at the intersection of the LD plot. Gray-blue boxes indicate less LD between evaluated variants. The polymorphic Alu element is in LD with the 2 TASs, rs2300747 and rs1335532. LD values between the TAS and the polymorphic Alu are shown to the right of the plot. (B) Minigene-splicing assay of CD58 locus. The CD58 genomic locus (gray box, also from A) with and without the Alu present (red) encompasses alternatively used exon 3. (C) Representative gel of splicing assay results showing 2 independent clones for each construct assayed. Two bands of indicated size were quantified from agarose gel. Data were combined with a second replicate and graphed with error bars indicating the standard deviation of the four values for each construct. The construct containing the polymorphic AluY was compared to the allele without an Alu present and constructs where the polymorphic AluY was replaced with the AluYa5 consensus sequence, scrambled Alu sequence (scrAlu), and spacer sequence with GC content matching the intron (rGC). The polymorphic AluY has the greatest effect but is not statistically different from the AluYa5 consensus or scrAlu-2. These 3 constructs (+Alu, Ya5, and scrAlu-2) are denoted with a * because they are all statistically different than the construct with the empty naturally occurring allele (no Alu). This indicates an effect of these sequences on splicing relative to the no Alu allele. They are also statistically different from all constructs without a * (unpaired t-tests, P< 0.05, adjusted). (D) Analysis of CD58 splicing at the endogenous locus. With primers that bind in CD58 exons 2 and 4, two spliced products, of indicated sizes, were detected at the endogenous locus. Individuals (n = 12) with noted Alu genotypes were evaluated. Graph shows quantification based on genotype with each individual indicated by a black circle. Error bars are the standard deviation within the group. An unpaired t-test indicates a dose dependent effect between genotypes and percent exon skipping was detected.