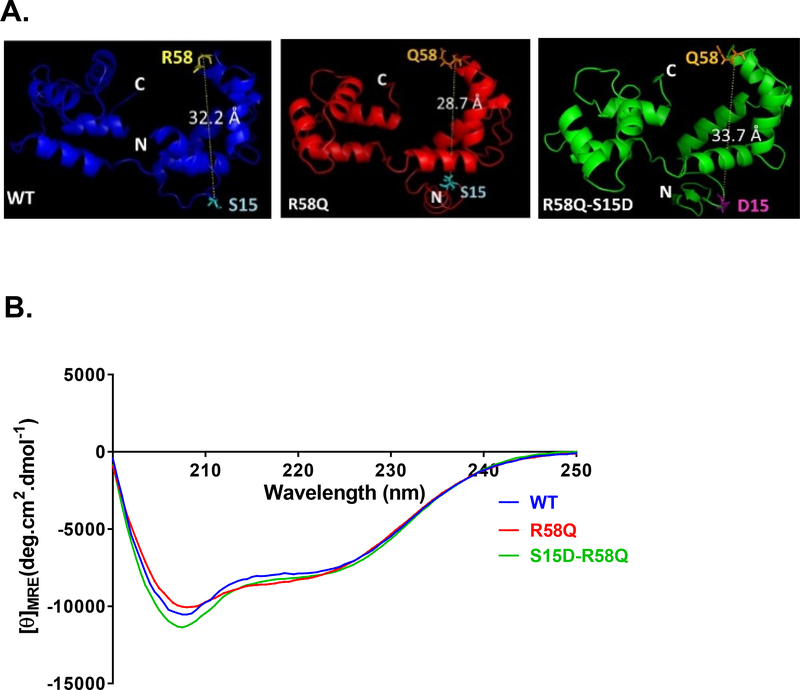
Figure 1.
A. Secondary structure predictions for HCRLC and mutants. Modeled structures of human ventricular RLC (MYL2) WT, R58Q and S15D-R58Q, using I-TASSER. Note that the distance between the C-α of R58 and S15 is changed in HCM-R58Q mutant and that the phosphomimic variant reverses this value to the level of WT. B. Effect of the R58Q mutation and S15D-R58Q phosphomimic on the CD spectra of human cardiac RLC. Far-UV CD was performed utilizing a 1-mm path quartz cell in a Jasco J-720 spectropolarimeter. Spectra were recorded at 190–250 nm with a bandwidth of 1 nm. [θ]MRE at 222 nm was used to calculate the α-helical content (fH) using the equation: [θ]222 = −30,300 fH − 2,340.