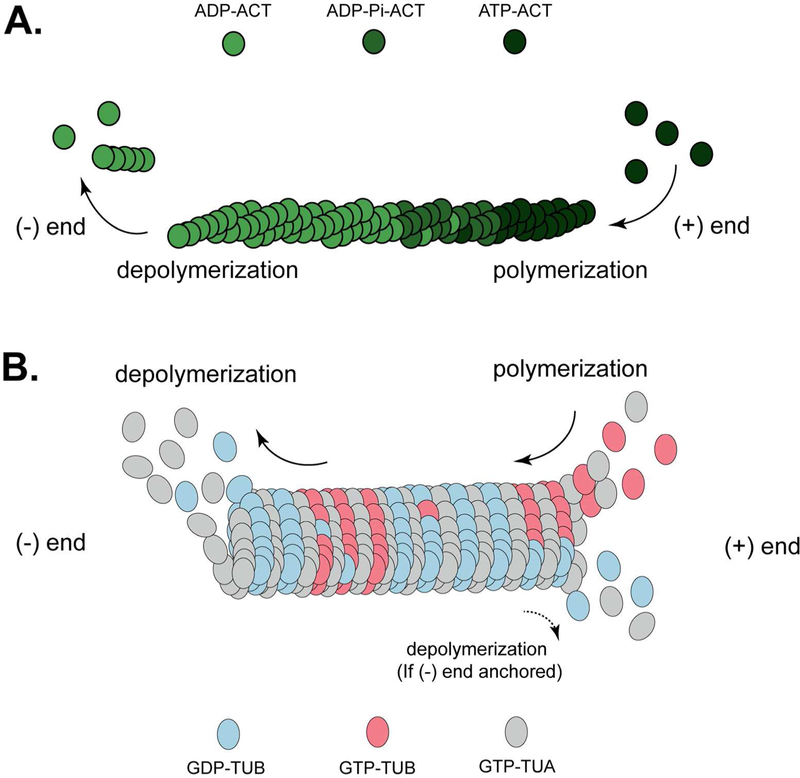
Fig. 1.
Schematic diagram of cytoskeleton polymerization/depolymerization (treadmilling). A, Microfilament treadmilling. G-actin is dynamically polymerized onto the growing F-actin strand. The (+) end is defined as the site where polymerization dominates, and the (−) end as where depolymerization dominates. Actin polymerization is achieved through loading ATP-associated G-actin to the end of F-actin, while depolymerization occurs through destabilization of ADP-associated actin. B, Microtubule treadmilling. The (+) end is defined as the site where polymerization dominates, while on the (−) end, tubulin is relatively stable with dominant depolymerization. In some cases, when the (−) end is anchored, the (+) end can also have stochastically dominant polymerization. α-tubulin (TUA) and β-tubulin (TUB) form a heterodimer as the basic unit of polymerized microtubule. TUA is constitutively bound to GTP; TUB binds the growing MT filament as GTP-bound monomers, and tends to disassociate from the filament when bound to GDP.