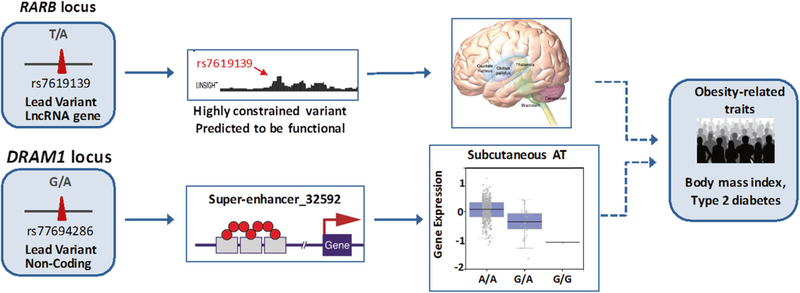
Fig. 2.
Biological insight of the two replicated variants in CHARGE. Data generated from an array of complementary approaches including genetic fine-mapping, epigenetic regulation and expression data to investigate the biological relevant of novel variants. Through genetic fine mapping, we showed that the lead variant at RARB locus associated with CHO intake was the best-ranked variant in the region. This variant is placed in a lncRNA, is a highly constrained variant and predicted to be deleterious. We showed that the lncRNA gene is differently expressed in several brain regions and is involved in neuronal progenitor cells differentiation. For DRAM1, the GWA hit is predicted to be the most likely causal variant in the region and lie in a superenhancer of DRAM1 (super-enhancer 32592). Gene-tissue expression showed that the allele associated with higher protein intake was associated with lower expression (rank normalized expression) of DRAM1 in subcutaneous adipose tissue (A/A; Homozygote reference, n = 359. G/A; Heterozygote, n = 29, G/G; Homozygote alternate, n = 1). The clinical transcendence of the two identified loci in CHARGE is supported by the association with obesity-related traits. DRAM1 findings did not replicate when using data from the UK Biobank data alone