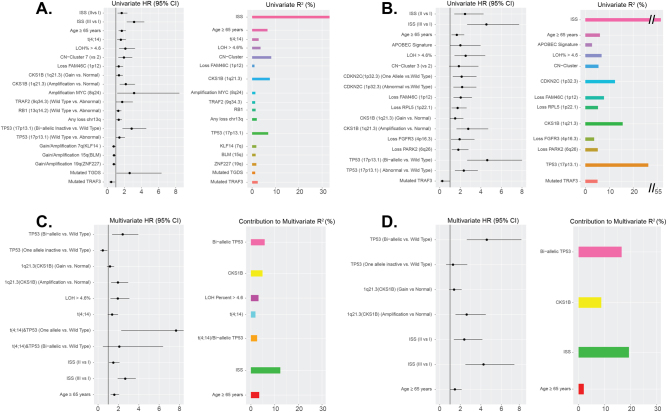
Fig. 3.
Molecular and clinical features associated with outcome. Significant associations of genetic and clinical factors with PFS (a) and OS (b) in univariate analyses. Covariates investigated include, age, ISS, IGH translocations, MYC translocation, APOBEC signature, hyperdiploidy, LOH%, homologous recombination deficiency mutations, copy number cluster, mutational data, copy number data, and bi-allelic inactivation data. Covariates significantly associated with at least one of PFS or OS (Wald P ≤ 0.05) in univariate models are presented. c The final multivariate model for PFS containing clinical and genetic factors has a cumulative R-squared of 34.3% compared to a cumulative R-squared of 18.4% for the model developed containing only genetic factors. d The final model for OS contains clinical and genetic factors, and has a cumulative R-squared of 46.5% compared to a cumulative R-squared of 25.2% for the model developed containing only genetic factors