Fig. 1.
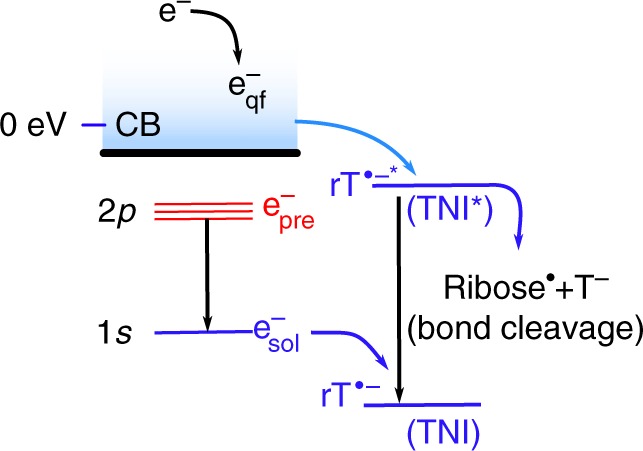
A schematic diagram of energy level showing different states of electrons during trapping and relaxation. These processes take place in a polar medium following ionizing radiation in the presence of ribothymidine (rT). An excess electron in the conduction band (CB), representing a quasi-free electron (eqf-), eventually becomes trapped (esol-) in the solvent cage. The excited state of esol- is considered as a "presolvated" electron, epre-. Electrons captured by solute molecules produce transient negative ions (TNI or rT•‒). The TNI in its excited state (TNI*) can either liberate the excess energy to the solvent (relaxation) or undergo bond breaking (dissociation)
