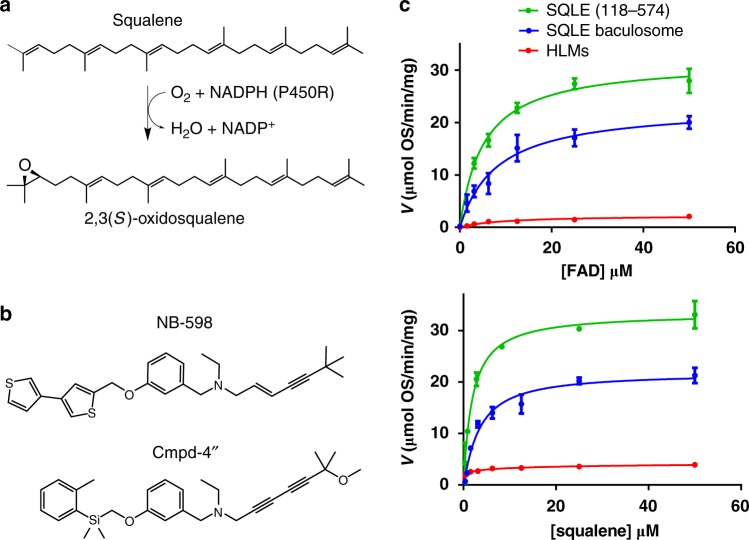
Fig. 1.
Structure of SQLE inhibitors and biochemical characterization of SQLE reaction. a Biochemical reaction catalyzed by SQLE. b Structures of SQLE inhibitors NB-598 and Cmpd-4′′. c Steady-state parameters for squalene and FAD affinity. Three experimental systems utilized correspond to the recombinant N-terminally truncated SQLE (118–574), baculosome membrane preparations from Sf9 cells overexpressing full-length SQLE, and human liver microsomes (HLMs) with endogenous SQLE. Enzyme concentrations were determined by immunoblotting and comparing to a standard curve of recombinant purified SQLE. Data obtained from enzymatic assays performed with saturating squalene and varied FAD or varied squalene and saturating FAD were fit to the standard Michaelis–Menten model to obtain KM values for each varied reaction component. Points and error bars denote the mean and standard deviation of triplicate measurements, respectively