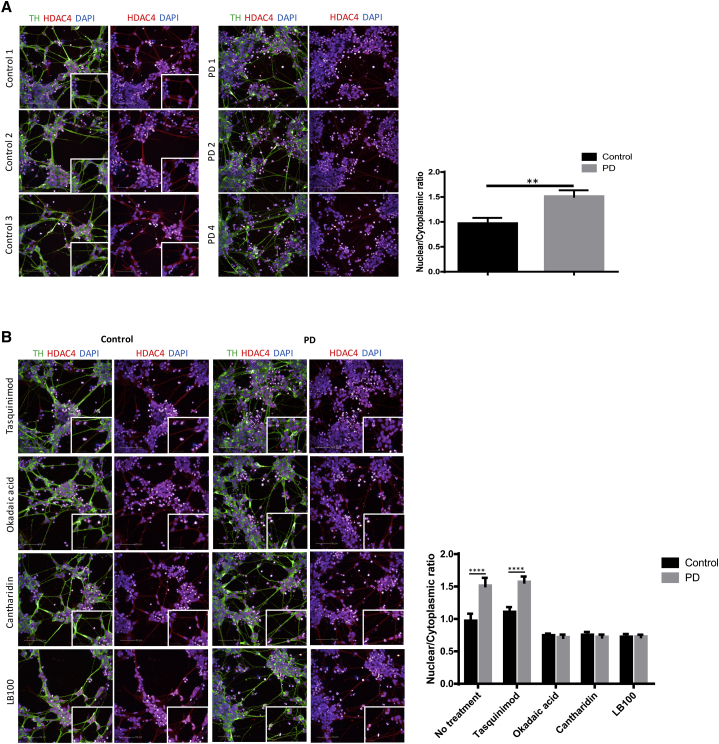
Figure 4.
Modulation of PP2A Activity Corrects HDAC4 Nuclear Mislocalization in PD GBA-N370S iPSC-Derived Dopamine Neurons
(A) Cytoplasmic and nuclear localization of HDAC4 in control and PD GBA-N370S dopamine neurons shown by immunofluorescence at 45 DIV—TH, green; HDAC4, red; DAPI, blue; HDAC4/DAPI nuclear colocalization, purple. The HDAC4 nuclear/cytoplasmic ratio is significantly increased in PD GBA-N370S patients. Data are represented as mean ± SD (∗∗p < 0.01).
(B) HDAC4 cellular localization in the presence or absence of tasquinimod (HDAC4 allosteric inhibitor) or okadaic acid, cantharidin, and LB-100 (PP2A inhibitors) at 45 DIV—TH, green; HDAC, red; DAPI, blue; and HDAC4/DAPI nuclear colocalization, purple. The three PP2A inhibitors correct HDAC4 nuclear mislocalization in PD GBA-N370S patient-derived dopamine neurons compared to no treatment. In contrast, tasquinimod, a HDAC4 allosteric inhibitor, has no effect on HDAC4 localization. Data are represented as mean ± SD (∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001).