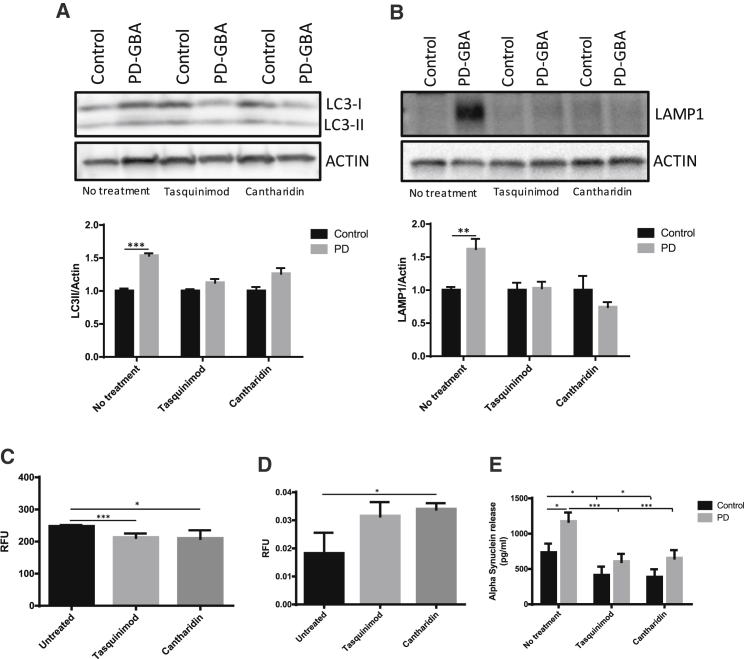
Figure 6.
Modulation of HDAC4 Activity or Localization Rescues Deficits in the Autophagic and Lysosomal Pathway and Reduces α-Synuclein Release in PD GBA-N370S iPSC-Derived Dopamine Neurons
(A and B) Modulation of HDAC4 activity by allosteric inhibition of HDAC4 (tasquinimod) or inhibition of PP2A (cantharidin) rescues the increase in autophagosomal (LC3-II; A) and lysosomal (LAMP1; B) compartments seen by western blot in PD GBA-N370S patient iPSC-derived neurons compared to controls.
(C) The reduction of lysosomes in PD GBA-N370S iPSC-derived dopamine neurons treated with tasquinimod or cantharidin was confirmed by a decrease in lysosome punctae by immunofluorescence.
(D) Modulation of HDAC4 increases lysosomal activity in PD GBA-N370S iPSC-derived neurons measured by DQ-BSA cleavage.
(E) Tasquinimod or cantharidin reduces the increase in α-synuclein release seen in PD GBA-N370S patient-derived neurons compared to controls.
Data are represented as mean ± SEM (∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01, and ∗∗∗p < 0.001).