Figure 7.
Nuclear Mislocalization of HDAC4 and Related Perturbations in Gene Expression Are Observed in Idiopathic PD Cases
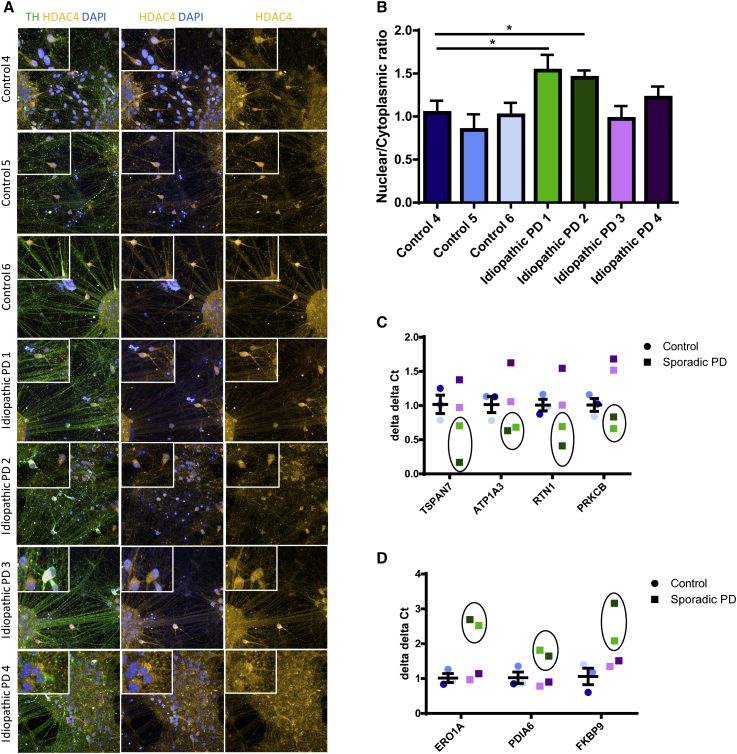
(A) Cytoplasmic and nuclear localization of HDAC4 in control and idiopathic PD iPSC-derived dopamine neurons shown by immunofluorescence at 45 DIV—TH, green; HDAC4, yellow; DAPI, blue.
(B) The HDAC4 nuclear/cytoplasmic ratio is significantly increased in two of the four idiopathic PD patients. Data are represented as mean ± SEM (∗p < 0.05).
(C and D) A (C) decrease in the expression of HDAC4-controlled genes: TSPAN7; ATP1A3; RTN1; and PRKCBI and an (D) increase in the expression of ER stress genes: ERO1A; PDIA6; and FKBP9 is observed in the same two idiopathic PD cases that display HDAC4 mislocalization.