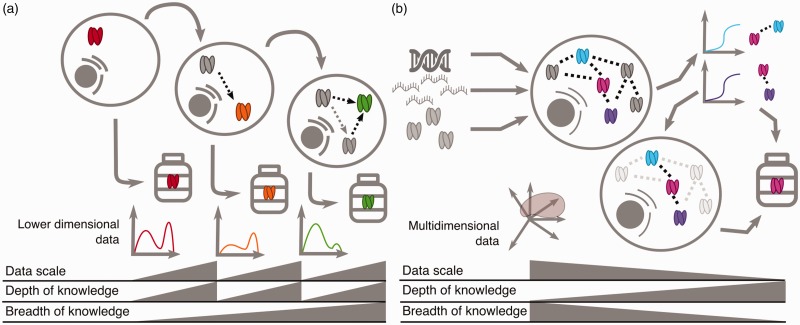
Figure 1.
A scientist engineer and reductionist biologist make different contributions to biological understanding. (a) The reductionist approach: a reductionist scientist serially perturbs a system and evolves a system schematic by characterizing individual component. At each phase, the reductionist scientist studies each component in greater depth. (b) The scientist engineer approach: a scientist engineer embraces the complexity of the system and starts with ‘omics’ level measurements to first derive a low-resolution map. At this early stage, the scientist engineer has many modeling techniques at their disposal including machine learning, statistical, and differential equations modeling. Later modeling tests the map and dedicated experiments refine relationships in the map. The scientist engineer first embraces complexity and then investigates single components in depth as needed. Iterative cycles of dedicated experiments update model assumptions and lead to new discoveries; only one cycle is depicted. In both examples, gray triangles indicate the relative magnitude of data scale, depth, and breadth of knowledge.