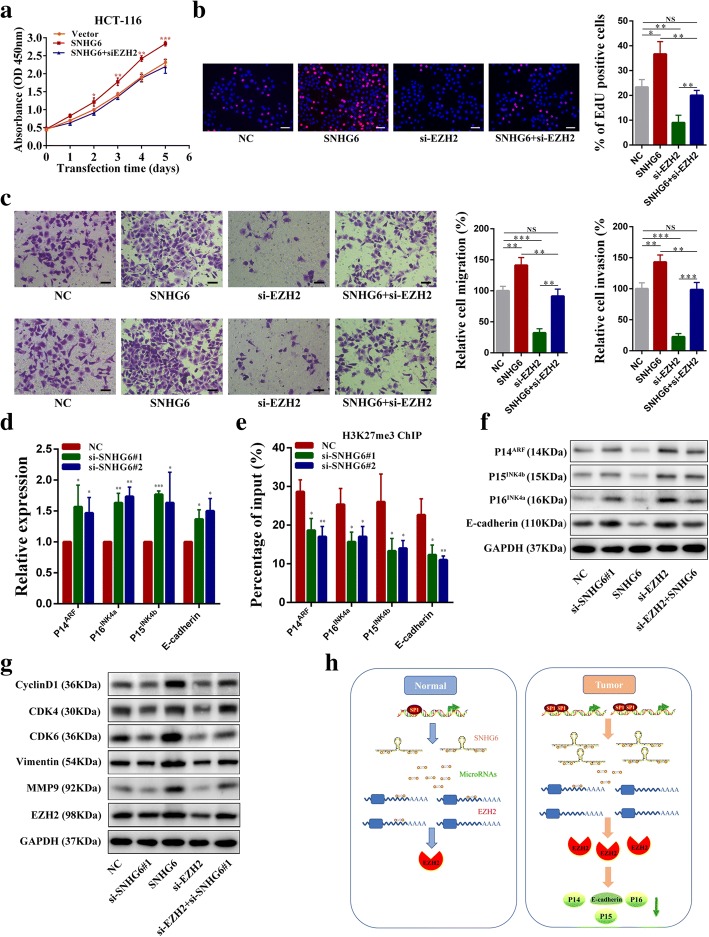
Fig. 8.
Tumor-promoting functions of SNHG6 is dependent on EZH2. a CCK-8 assays demonstrated that overexpression of SNHG6 promoted cancer cell growth. EZH2 knockdown could abolish growth promotion caused by SNHG6. b EdU assays showed that EZH2 knockdown abolished the increased proliferation rates of HCT-116 cells caused by SNHG6. c Transwell assays demonstrated that EZH2 knockdown abolished the increased abilities of migration and invasion caused by SNHG6. d Expression of P14ARF, P15INK4b, P16INK4a, and E-cadherin was detected by qRT-PCR in SNHG6-silenced HCT-116 cells. e ChIP assays revealed enrichment of H3K27me3 on promoter regions of P14ARF, P15INK4b, P16INK4a, and E-cadherin. f Expression of P14ARF, P15INK4b, P16INK4a, and E-cadherin was detected by western blotting in SNHG6-silenced HCT-116 cells. g The EZH2, cell cycle-related proteins, and metastasis-related proteins were detected by western blotting. h Schematic of the proposed mechanism of SNHG6 in CRC. Scale bar = 50 μm. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, and ***P < 0.001