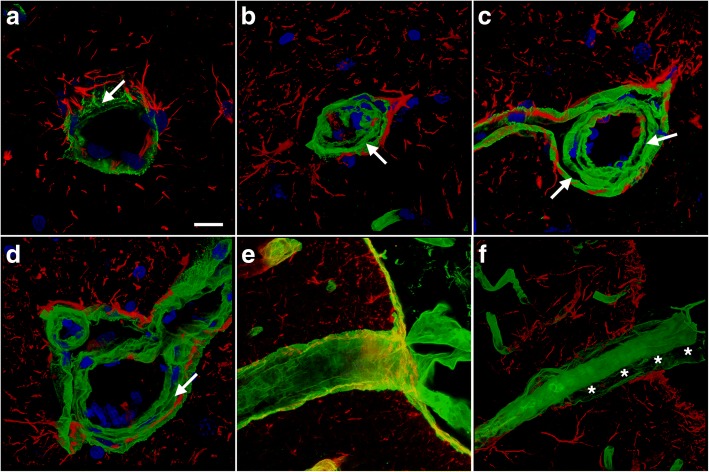
Fig. 10.
Altered vascular extracellular matrix in blast-exposed animals. Brain sections of rats euthanized 6 weeks after blast exposure were immunolabeled for collagen IV (green) and GFAP (red) with DAPI nuclear staining (blue). Arrows in the panels indicate the collagen IV-rich layers, which include the endothelial basal membrane and adventitia. a-d Representative sections from the hippocampal stratum lacunosum moleculare from a control (a) and a blast-exposed rat (b-d). Note the separation of the collagen IV-rich layers in panels (b-d), resulting in a multilayered appearance of the collagen IV- immunostained extracellular matrix. In panel (b) the loss of structure in the collagen IV-rich layers resulted in collapse of the lumen. e-f Penetrating cortical vessels from control (e) or blast-injured (f) rats. The blast-exposed vessel in panel (f) exhibits a double-barreled appearance. Asterisks (*) in panel (f) mark the separation of the adventitial layer from the tunica media of the blood vessel. Scale bar, 20 μm