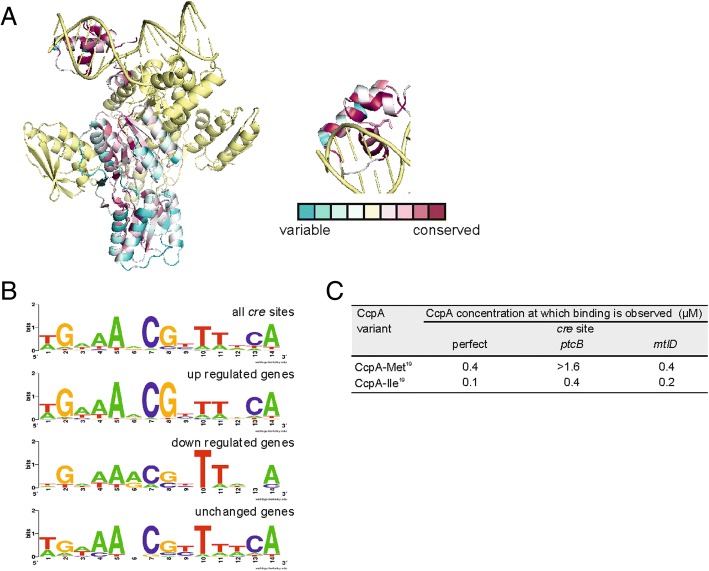
Fig. 6.
Mutations in ccpA result in increased binding affinity for certain cre sites. Mutations in the Met19 codon in the DNA binding domain of CcpA alter the binding affinity of CcpA for certain cre sites. a Using consurf db [43] and the B. subtilis CcpA-HPr complex bound to a synthetic cre site (3OQN) as a starting structure, the level of amino acid sequence conservation among LacI transcriptional regulators was analysed. One molecule of CcpA is colored according to the level of conservation within the LacI family of transcriptional regulators while the other molecule, HPr and the DNA are colored yellow. Dark purple indicates 100% conservation while blue indicates extensive sequence variation. The inset shows a view of the DNA-binding domain with the side chain of Met19 is shown. b Sequence logo diagrams representing the abundance and position of nucleotides in the CcpA-regulated genes of L. lactis MG1363. c Binding of CcpA to cre sites in vitro. The binding of CcpA-Met19 and CppA-Ile19 was tested with DNA sequences identified as cre sites upstream of ptcB and mtlD as well as a perfect cre site. As a negative control the CodY recognition site upstream of oppD was also tested (See also Additional file 1: Figure S6)