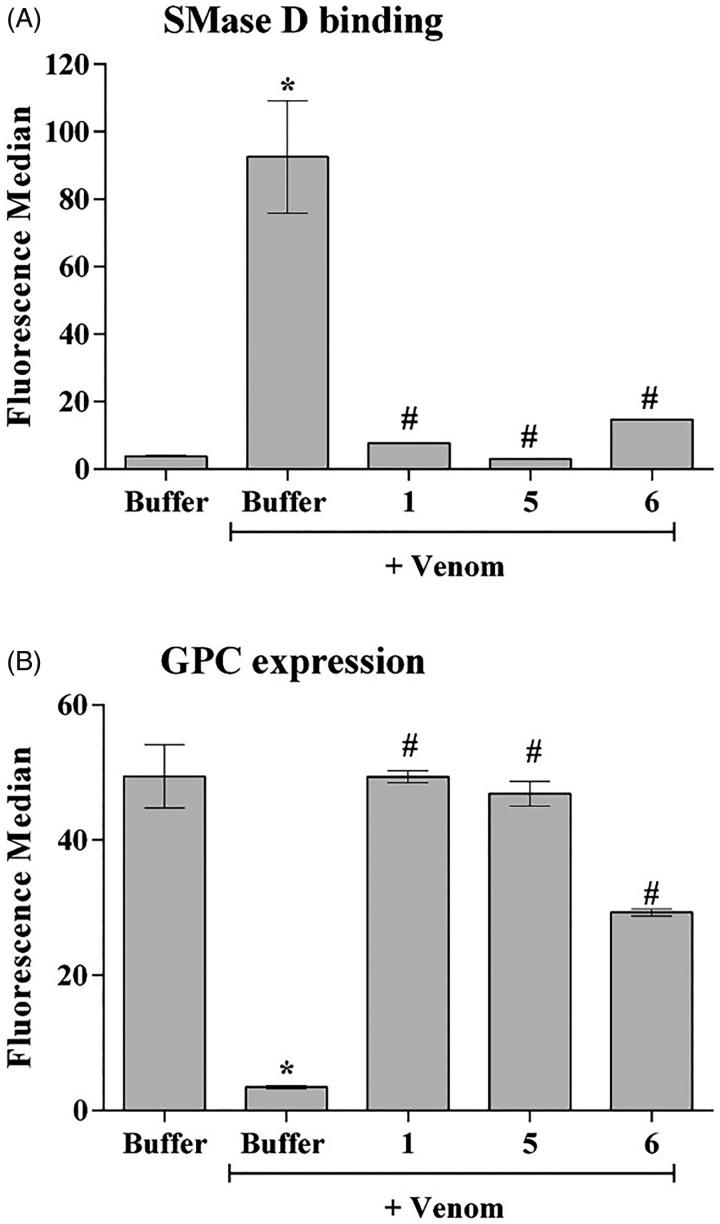
Figure 3.
The ability of the compounds to inhibit the binding of SMases D to the surface of erythrocytes and to induce the cleavage of glycophorin C (GPC). Human erythrocytes were treated with 2.5 μg of the L. laeta venom incubated or not with 20 μg of each inhibitor and analysed for the expression of GPC by flow cytometry. The ability of the toxins to bind to the surface of the erythrocytes was analysed using a rabbit monospecific polyclonal serum against L. intermedia SMases D. (A) Binding of SMase D on the surface of human erythrocytes. (B) Removal of GPC induced by L. laeta venom. Data are presented as mean ± SEM of duplicates representative of two independent experiments. The statistical analyse was performed by One-Way ANOVA followed by Tukey HSD test. (*)Significant difference in relation to the buffer (p < .05). (#) Significant difference in relation to L. laeta venom (p < .05).