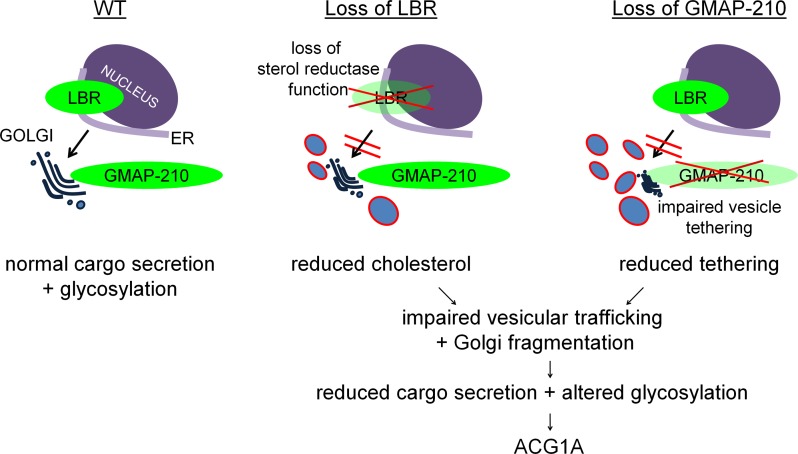
Figure 9. LBR and GMAP-210 deficiency impair vesicular transport in the early secretory pathway and cause defective glycoprocessing by the Golgi apparatus.
Left: Wild-type cells. Middle: LBR localizes to the nuclear envelope and to the endoplasmic reticulum (ER), functioning in lamin/chromatin-binding and as a sterol reductase. Loss of LBR impairs de novo synthesis of cholesterol and causes disruption of cholesterol-sensitive ER/Golgi trafficking, resulting in defective posttranslational glycan processing and Golgi vesiculation. Right: GMAP-210 is a tether for transport vesicles at the cis-Golgi and is required to maintain Golgi structure. Loss of GMAP-210 also leads to disruption of ER/Golgi trafficking, impaired glycan processing, and Golgi vesiculation. Thus, both lesions converge on Golgi organization and function in achondrogenesis 1A (ACG1A).