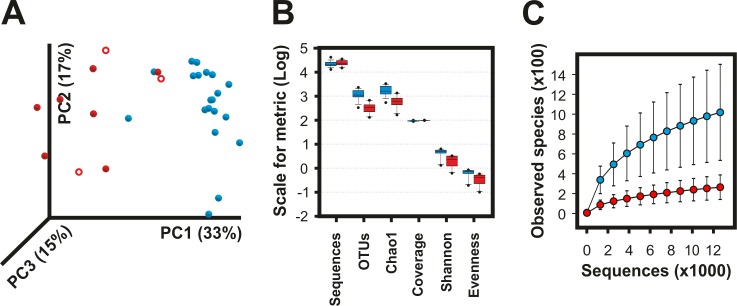
Fig 5. Collapse of the vaginal microbiome in cows developing postpartum endometritis.
Differences in the vaginal microbiome of cows developing postpartum endometritis (red; borderline: open symbols) and healthy cows (blue) were captured by 454 pyrosequencing of the v1-v3 16S rRNA at 7 days postpartum. OTUs at 97% of identity were generated in QIIME 1.8 using the pick_de_novo_otus.py pipeline. A) Principal components analysis showing a clear separation of samples by health status. B) Box plot summary of the diversity metrics of the vaginal microbiome showing lower richness and lower diversity in animals that developed postpartum endometritis (See S2 Table). C) Rarefaction analysis of observed species. The curves represent the average of each group. Error bars are the standard error of the corresponding groups. Healthy N = 20 and Endometritis N = 10. Clinical assignments were made at 21 DPP or later based on the vaginal mucus score.