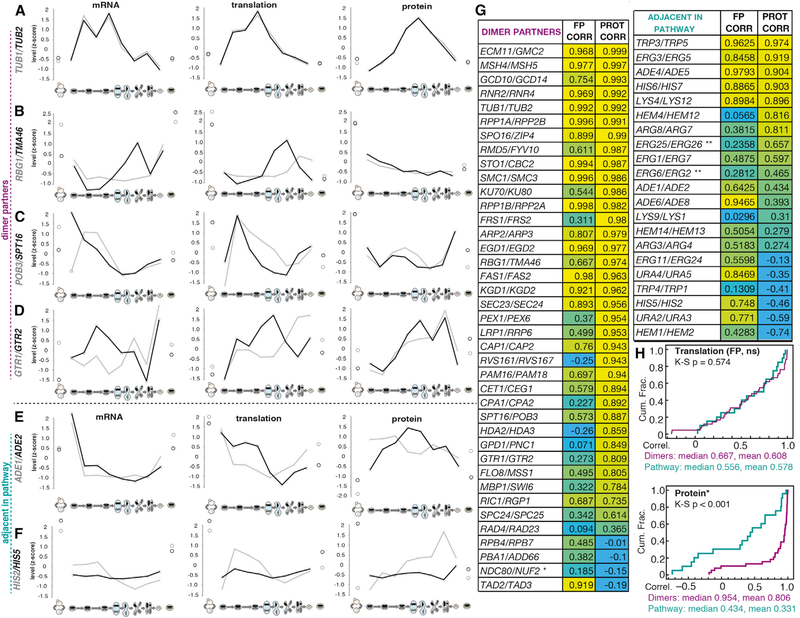
Figure 3. Meiotic Cells Are Capable of Perfect Synthesis Matching of Heterodimer Partners, but It Is Uncommon.
(A–F) Z-score plots show gene expression level trends of mRNA levels (left), translation levels (middle), and protein levels (right) over all time points for pairs of genes, including (A) heterodimer Tub1 and Tub2, (B) heterodimer Rbg1 and Tma46, (C) heterodimer Pob3 and Spt16, (D) heterodimer Gtr1 and Gtr2, (E) sequential enzymes involved in purine nucleotide biosynthesis Ade1 and Ade2, and (F) sequential enzymes involved in histidine biosynthesis His2 and His5.
(G) Correlation coefficients for translation and protein between annotated heterodimer partners are shown at left. Yellow represents higher, blue represents lower. The same scaling is used at upper right to compare to a subset of sequential enzymes in biosynthetic pathways. Below right, a summary of trends for heterodimers and adjacent enzymes in biosynthetic pathways. Heterodimer partners show a greater protein than translation correlation, while sequential biosynthetic enzymes show the opposite trend.
(H) Cumulative distribution plots for the translation and footprint correlations in (G). Translation correlations are indistinguishable for the heterodimers and biosynthetic pathway genes, but protein correlations are significantly higher for the heterodimers as assessed by the Kolomogorov-Smirnov (K-S) test.
See also Figures S2, S3, and S4.