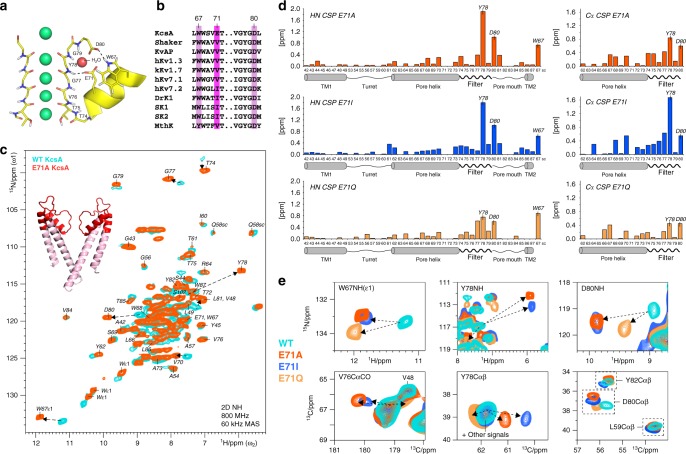
Fig. 1.
E71X point-mutations cause large conformational changes in the KcsA selectivity filter. a The selectivity filter of K+ channel KcsA (1K4C) is regulated by a hydrogen bond network with the triad W67–E71–D80 at the centre5. b W67 and D80 are highly conserved, while E71 is commonly replaced by a nonpolar valine or isoleucine in Kv channels. c 2D NH ssNMR spectra of WT KcsA (cyan) and mutant E71A (red) acquired in membranes. Arrows indicate major signal shifts of key residues. Residues L41–W87 are annotated in the E71A spectrum and highlighted in red on the X-ray structure. d Chemical shift perturbations (CSPs) of E71A (red), E71I (blue), and E71Q (orange) in reference to WT KcsA. Combined HN CSPs (left) of amino-protons and backbone-nitrogens and (right) Cα CSPs. The strongest NH CSPs in E71A are highlighted in c. Source data are provided as a Source Data file. e 2D NH (upper panel) and 2D CC spectra (lower) showing large CSPs of key residues W67, V76, Y78, and D80 in E71A (red), E71I (blue), and E71Q (orange) relative to WT KcsA (cyan)