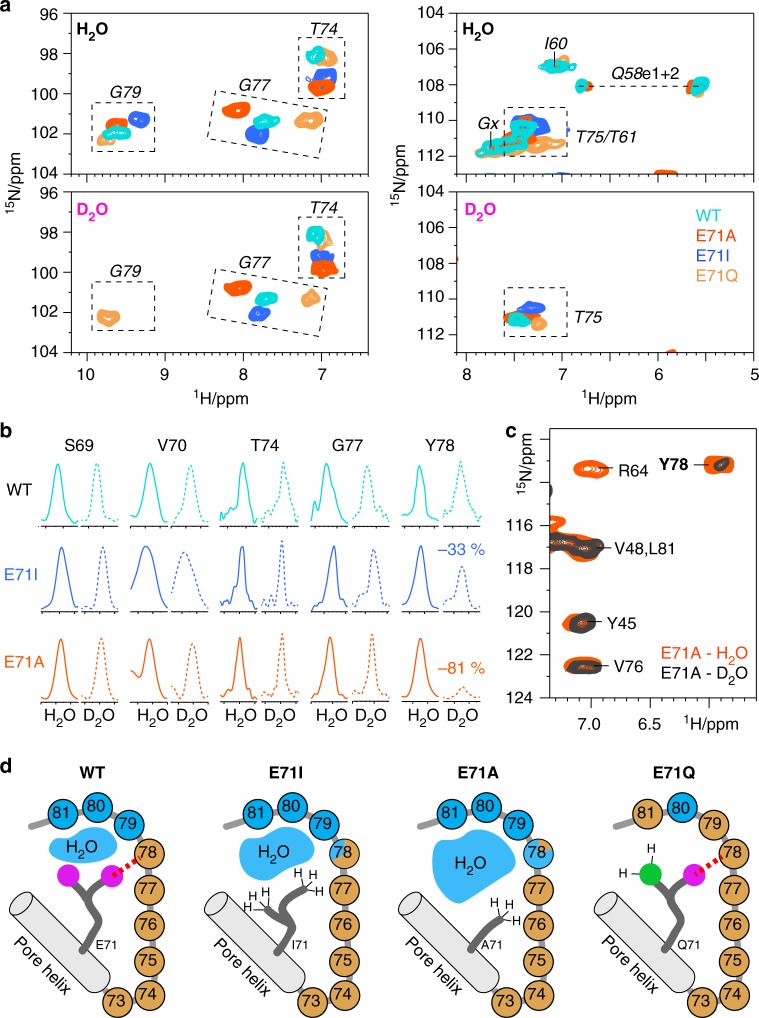
Fig. 4.
High-resolution analysis of the size of the water cavity behind the filter. a Zoom into 2D NH ssNMR spectra acquired in (upper panel) protonated and (lower) deuterated buffers of WT KcsA (cyan), E71I (blue), E71A (red), and E71Q (orange). b Cross-sections from 2D NH spectra of WT KcsA, E71I, and E71A measured in protonated (continuous lines) and deuterated (dashed) buffers. For Y78 in WT KcsA, cross-sections were extracted from 3D CANH experiments to resolve spectral overlap. Signals are normalised (see Methods). c 2D NH spectra of E71A in protonated (red) and deuterated (grey) buffers showing the fast exchange of Y78, implying a larger water cavity. d Illustrations of the ssNMR-derived water cavity size: in WT KcsA, the cavity is limited to G79-L81, and Y78 is exchange-protected. The cavity widens in E71I, strongly widens in E71A, and is absent in E71Q. Blue and brown spheres represent water-exposed and shielded amino-protons, respectively