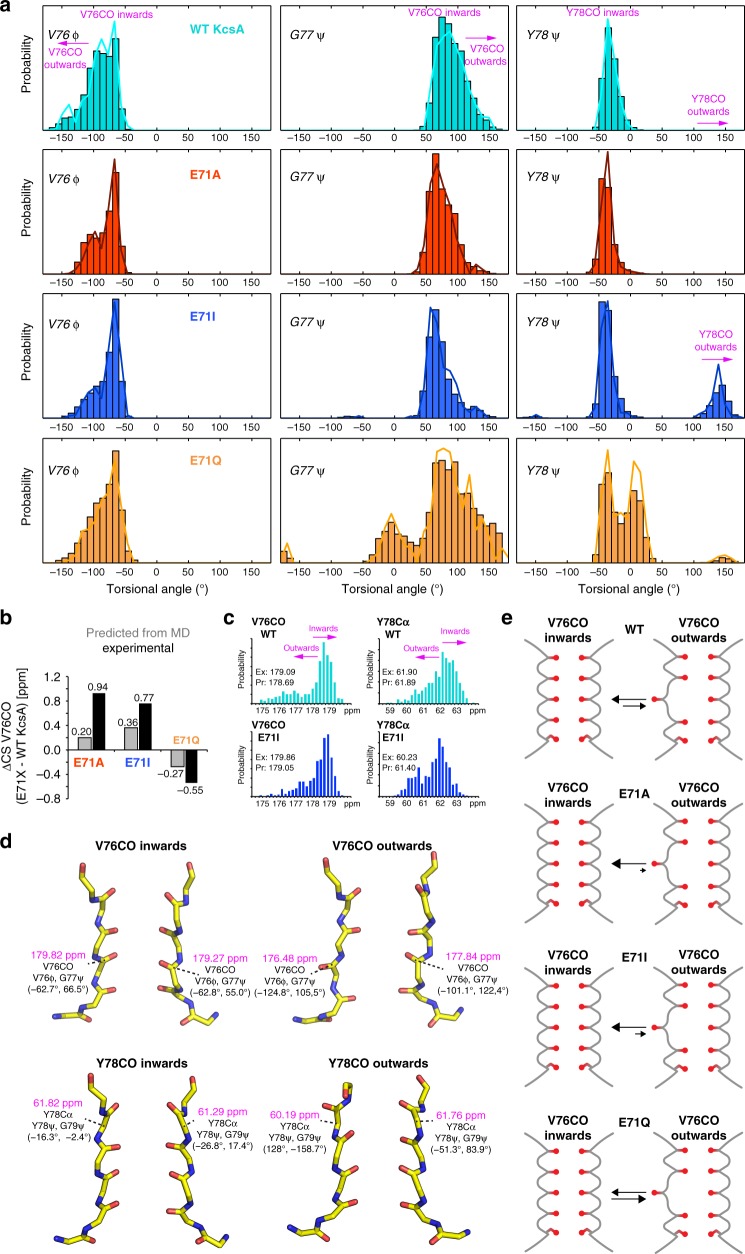
Fig. 5.
E71X mutations shift the equilibrium between inwards and outwards filter states. a Dihedral angle distribution of filter residues of WT (cyan), E71A (red), E71I (blue), and E71Q (orange) derived from 1-μs-long MD simulations. Characteristic angular spaces for inwards conformations, with the carbonyl group oriented towards the filter pore, and outwards states are highlighted. b Comparison of V76CO CSPs derived from experiments (black bars) and back-calculated36 from MD simulations (grey bars). Source data are provided as a Source Data file. c Histogram of back-calculated chemical shifts for V76CO and Y78Cα of WT KcsA (cyan) and E71I (blue). The V76CO (left) inwards state is stabilised in E71I, leading to higher V76CO chemical shifts, while the Y78CO (right) inwards state is destabilised in E71I, leading to lower Y78Cα chemical shifts. d Representative MD snapshots of WT KcsA and E71I showing inwards and outwards states of V76CO and Y78CO. The chemical shifts (in magenta) of V76CO and Y78Cα strongly differ between inwards and outwards conformations. e Illustration of the stabilisation of the V76CO inwards state in E71A and E71I, and the destabilisation in E71Q