Fig. 2.
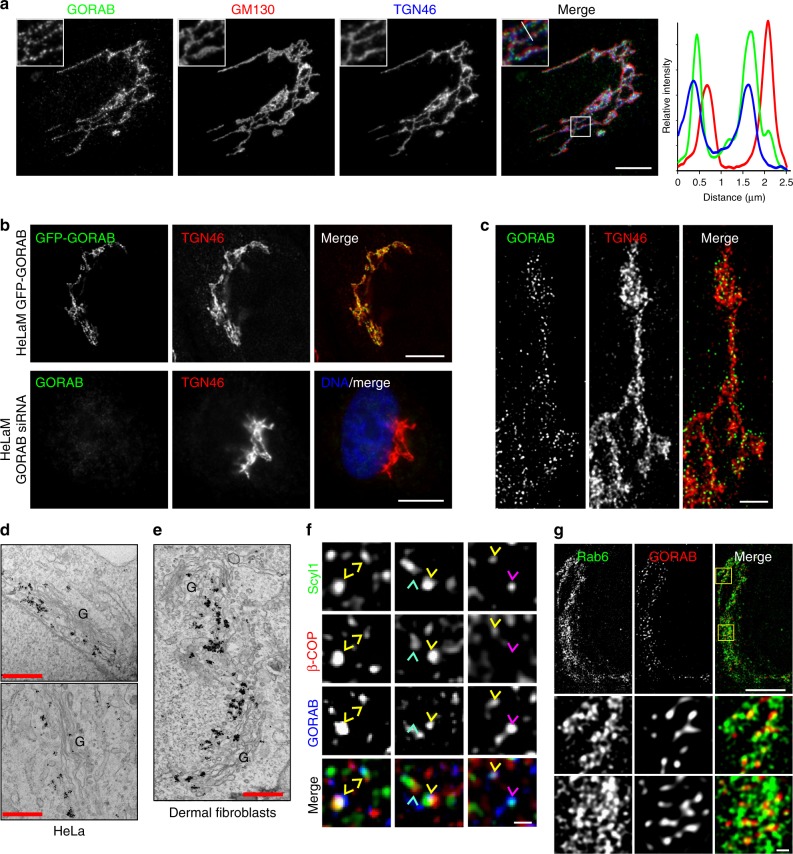
GORAB co-localizes with Scyl1 and COPI in discrete domains at the trans-Golgi. a Analysis of GORAB localization at the Golgi. Human dermal fibroblasts were fixed and labeled with antibodies to GORAB, GM130 and TGN46. Scale bar, 10 µm. The linescan is representative of data from n = 20 cells. b Analysis of GFP-GORAB localization in stably transfected HeLaM cells (top) and in HeLaM cells transfected with GORAB siRNA (bottom). Cells were fixed and labeled with antibodies to GORAB (bottom row only) and TGN46. Scale bar, 10 µm. c GORAB Golgi localization using STED microscopy. Human dermal fibroblasts were fixed and labeled with antibodies against GORAB and TGN46. Scale bar, 1 µm. d, e Representative EM micrographs depict localization of GORAB in HeLa cells (d) and human dermal fibroblasts (e). G Golgi. Scale bars, 500 nm. f Co-localization analysis of GORAB, Scyl1 and β’-COP using STED microscopy. Human dermal fibroblasts were fixed and labeled with antibodies against Scyl1, GORAB and β’-COP. Scale bar, 200 nm. Yellow arrowheads mark GORAB puncta co-localizing both with Scyl1 and β’-COP, magenta arrowheads mark GORAB puncta co-localizing with Scyl1 only and cyan arrowheads mark Scyl1 puncta co-localizing with ⍰’-COP but devoid of GORAB. g Co-localization analysis of GORAB and Rab6 using STED microscopy. Human dermal fibroblasts were fixed and labeled with antibodies against GORAB and Rab6. Top, scale bar, 5 µm, bottom, scale bar, 200 nm