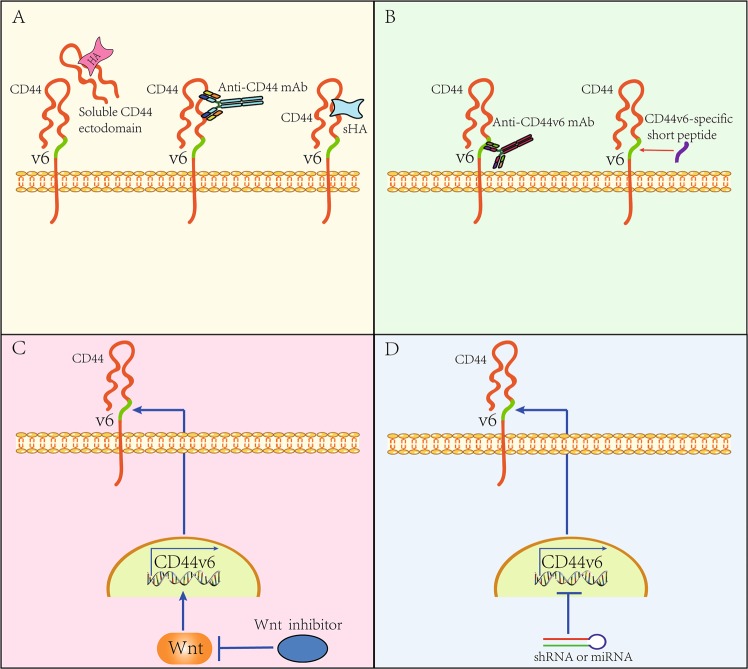
Fig. 5. The strategies of anti-CD44v6 therapy.
a The strategy of anti-CD44v6 therapy by blocking the interaction between HA and CD44v6. Furthermore, the soluble CD44v6 ectodomain is used for blocking HA binding, and the anti-CD44 mAb is used for blocking the HA-binding epitope on the CD44v6 ectodomain. In addition, the small fragment of HA (sHA) is able to inhibit the binding of HA to the CD44v6 ectodomain as well. b The strategy of anti-CD44v6 therapy by blocking the proximal membrane region encoded by the variant exon 6. Thus, the anti-CD44v6 mAb and CD44v6-specific peptide are available. c The strategy of anti-CD44v6 therapy by antagonizing the Wnt signaling pathway. Furthermore, the CD44v6 expression is driven by the activation of canonical Wnt (see ref. 36). Selective inhibition of Wnt by using small-molecule compounds potently suppresses the CD44v6 production (see ref. 71). d The strategy of anti-CD44v6 therapy by using shRNA or miRNA. Either miRNA or shRNA can effectively limit the CD44 gene expression, thus reducing the production of CD44v6 (see ref. 3,5)