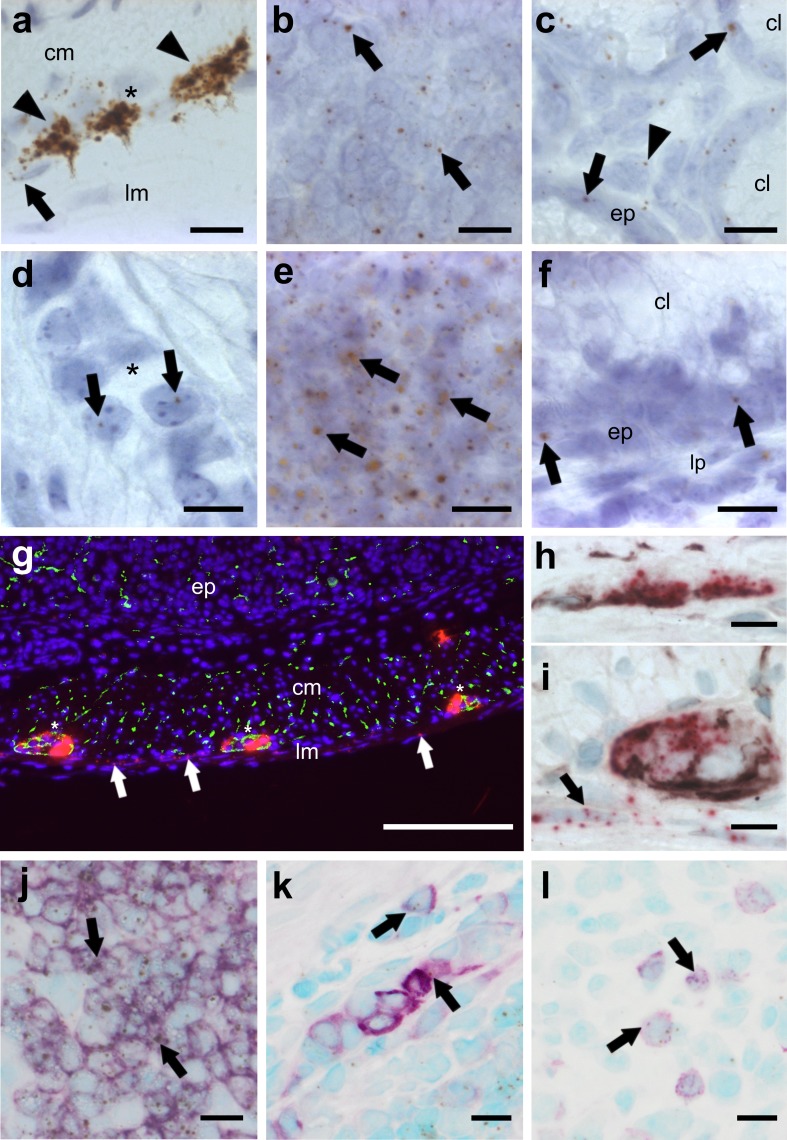
Fig. 1.
ISH staining of CB1 (a–c, g–i) and CB2 (d–f, j–l) mRNA in the colon of healthy mice. CB1 mRNA is strongly detected in neurons of the myenteric (a brown, DAB, arrowheads; i FastRed) and the submucosal plexus (h FastRed). CB1 gene expression is also found in the longitudinal muscle layer (a, g, iarrows), in lymph follicles (b arrows) and to a lesser degree in epithelial cells (c arrows) as well as some cells of the lamina propria (c, arrowhead). In contrast, CB2 gene expression is scarcely found in the myenteric plexus (d arrows). Highest expression of the CB2 gene occurs in lymph follicles (e arrows), whereas low expression is seen in epithelial cells (fep) and the lamina propria (flp). CB1 mRNA fluorescence staining (FastRed) shows modest co-localization (yellow) with synaptophysin (green) in the myenteric plexus (g plexus denoted by asterisks). CB1 mRNA (FastRed) shows clear co-localization with neurofilament H (brown, VIP) in the submucosal (h) as well as in the myenteric (i) plexus. CB1 mRNA is also found in the longitudinal muscular layer where it does not co-localize with either of the neuronal markers (arrows in g and i). CB2 mRNA (brown, DAB) is predominantly detected in B220+ cells (purple, VIP) of lymph follicles (j) and only marginally in F4/80+ (k) or CD3+ (l) cells. Calibration bars: a–f, h–l 10 µm, g 200 µm; cm circular muscle layer, ep epithelium, lp lamina propria, lm longitudinal muscle layer, cl crypt lumen; *, myenteric ganglion; arrows point at representative cells expressing CB1 or CB2 genes