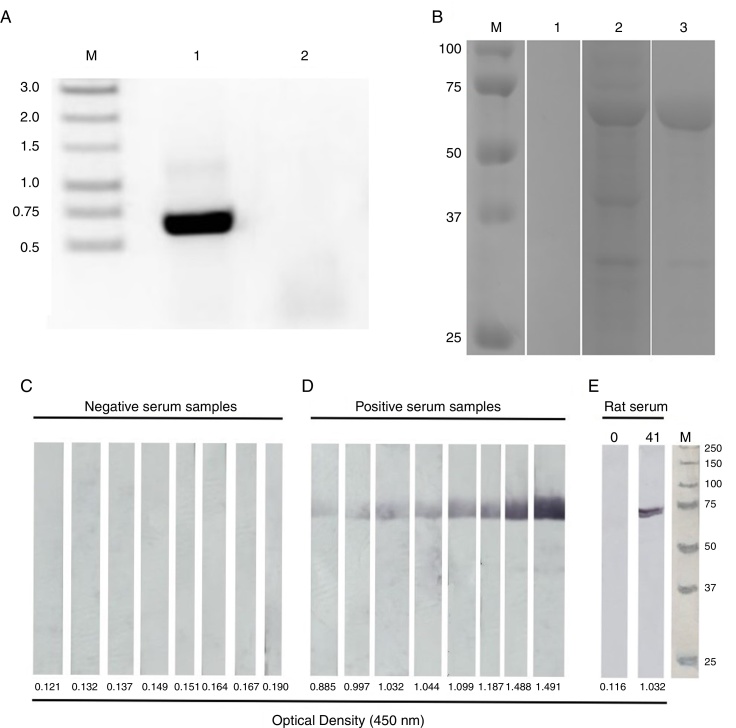
Fig. 1.
(A) Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) amplification of the nucleotide sequence corresponding to the BLV capsid protein gene. Lymphocytes from BLV-infected cows (lanes 1) and from a non-infected cow (lane 2) were used for DNA extraction and analyzed by PCR. The fragment amplified was 666 nucleotides in length. M: 1 Kbp molecular weight markers. (B) Analyses of the recombinant BLV capsid protein (BLV p24r). Samples were collected prior to IPTG induction (lane 1), after overnight induction (lane 2), and after purification by the HisTrap column (lane 3), analyzed by SDS-PAGE and stained by Coomassie blue. The size of the molecular weight markers is indicated on the left side. (C) Western blot analysis of the BLVp24r protein. The purified BLVp24r protein resolved by SDS-PAGE and transferred to nitrocellulose membrane. Membrane strips containing the BLVp24r were incubated with serum from non-infected (panel C; n = 8) and naturally BLV-infected (panel D; n = 8) cows, and with rat serum (panel E) collected prior to (day 0) or after immunization (day 41) with the BLVp24r. All sera were also evaluated by our in house iELISA and the optical density (OD450 nm) of each serum is indicated below the strips. M: molecular weight markers.