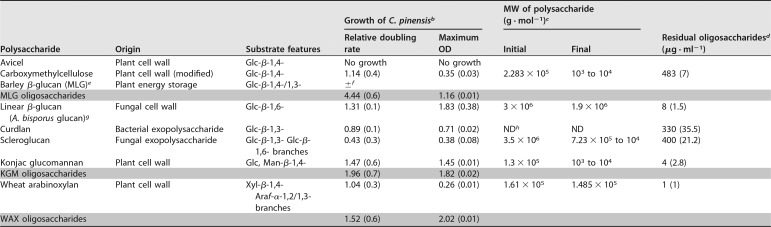
TABLE 1.
Deconstruction of carbon sourcea
Carbon source was included in the medium at 5 g · liter−1 at the start of cultivation. The shaded rows show data for oligosaccharides produced by preincubating polysaccharides with an appropriate endo-acting glycoside hydrolase. Two biological replicates were performed for each experiment, and standard deviations (SD) are shown in parentheses. Cultures were regularly sampled to assess the deconstruction of polysaccharides. Growth curves for konjac glucomannan and wheat arabinoxylan were presented in reference 13.
bGrowth is given as the doubling rate for growth on a polysaccharide divided by the doubling rate for growth on glucose (i.e., a relative doubling rate of >1 indicates that growth was faster for this carbon source than for glucose).
cApproximate average molecular weight (MW) of polysaccharides was calculated from data obtained by SEC-MALLS analysis (see Fig. S1 in the supplemental material). Changes in average MW show the extent to which the polymers were degraded.
dOligosaccharides remaining in the liquid growth medium following the final stages of growth were analyzed by HPAEC-PAD (see Fig. S2 for the exact time point at which these samples were taken). Structures were quantified based on the peak area of the most closely eluting appropriate linear standard.
eMLG, mixed-linkage β-glucan.
f±, some growth was observed, but it was too slow to be measured.
gA. bisporus glucan, a linear β-glucan from Agaricus bisporus.
hND, not determined due to solubility issue.