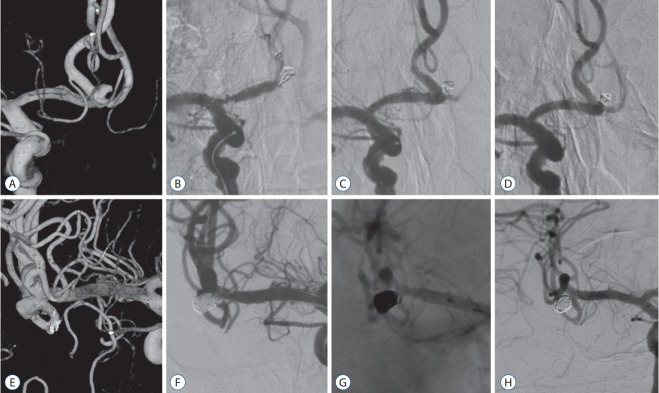
Fig. 3.
Cases of thromboembolic complication. A-D : A case of anterior communicating artery aneurysm. A : The anterior communicating artery aneurysm has a wide neck. B : Change in vascular geometry and wrinkling of proximal A1 segment with distal flow stagnation by stent deployment is observed. The angle between A1 and A2 is changed compared to that in Fig. 3A. C : Note the restored vascular geometry and patent arteries after stent removal. D : Follow-up angiography at 3 years shows stable and complete embolization and patent parent arteries. E-H : A case of middle cerebral artery aneurysm. E : A wide-necked middle cerebral artery bifurcation aneurysm incorporating inferior trunk. F : At the final stage of stent-assisted coil embolization of the aneurysm, thrombosis occurrs in the origin of inferior trunk. G : The stent is removed safely and chemical thrombolysis is performed to achieve full recanalization. H : Follow-up angiogram at 5 years shows completely embolized aneurysm with patent inferior trunk.