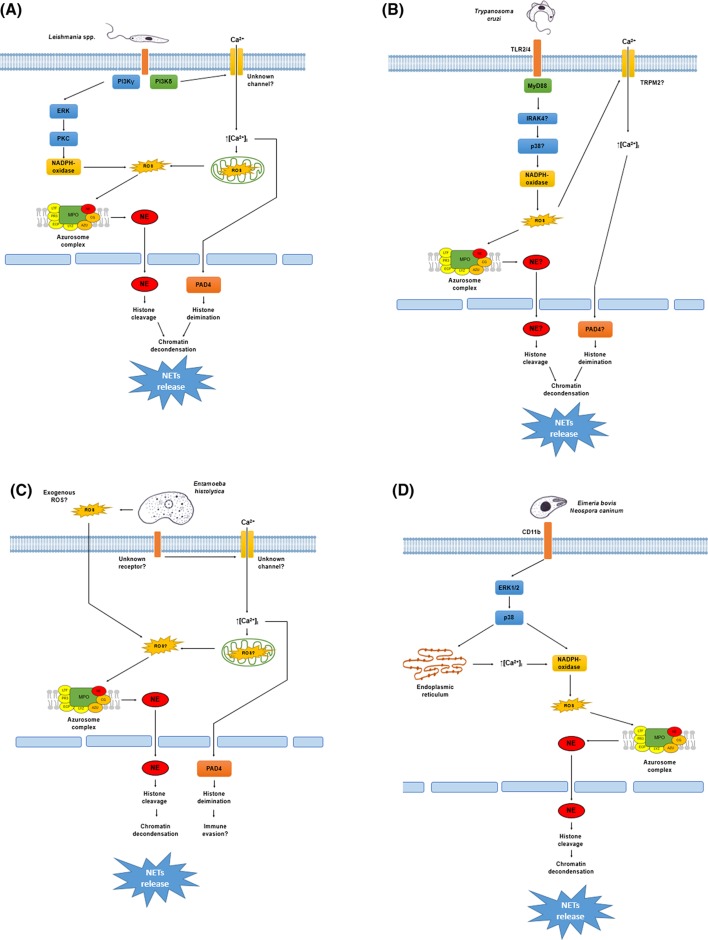
Figure 1. NETosis mechanisms triggered by protozoan parasites.
(A) Leishmania spp. promastigotes activate the PI3K signal pathway. PI3Kγ isoform leads to activation of the ERK pathway that phosphorylates PKC promoting the NADPH oxidase assemble. The NADPH oxidase generates ROS causing oxidative dissociation of the NE from the azurosome complex present in the membrane of azurophilic granules. NE is translocated to the nucleus where this enzyme cleaves the histones promoting chromatin decondensation and NET release. The PI3Kδ isoform probably causes calcium influx through an unknown membrane channel promoting ROS generation from the mitochondrial respiratory chain. ROS lead to the nuclear translocation of NE as mentioned above, or the influx of calcium activates the PAD4 causing histone citrullination and chromatin decondensation. (B) Trypanosoma cruzi trypomastigotes are sensed by the TLR2/4 receptor complex leading to NADPH oxidase assemble via the MyD88/IRAK4/p38 pathway. ROS promote NE translocation to the nucleus from the azurosome complex or activate the TRPM2 channels leading to calcium influx, which activates PAD4. Both pathways converge in the chromatin decondensation and NET release by histone cleavage or histone citrullination, respectively. (C) Entamoeba histolytica trophozoites trigger NETosis dependent on NE activity and extracellular calcium influx but independent of NADPH oxidase-derived ROS. It is likely that other ROS sources could be implicated in NETosis induced by amoebas since exogenous ROS from trophozoites or ROS from the mitochondrial respiratory chain can promote NE translocation, chromatin decondensation, and NET release as described elsewhere. In contrast, the trophozoites cause calcium influx that activates PAD4 promoting protein citrullination. Since PAD4 activity is not necessary for NETs release by amoebas, protein citrullination could be a mechanism of the parasite to evade the anti-microbial action of NETs. (D) The Apicomplexa parasites Eimeria bovis and Neospora caninum are sensed by neutrophils throughout the CD11b receptor, which in turn activates the ERK1/2 signaling pathway. The ERK pathway leads to calcium mobilization from the storages operated calcium entry (SOCE) that promotes NADPH oxidase activation or directly promotes NADPH oxidase assemble by phosphorylation. ROS are generated from this complex and the NE translocation takes place to decondense chromatin for release of NETs.