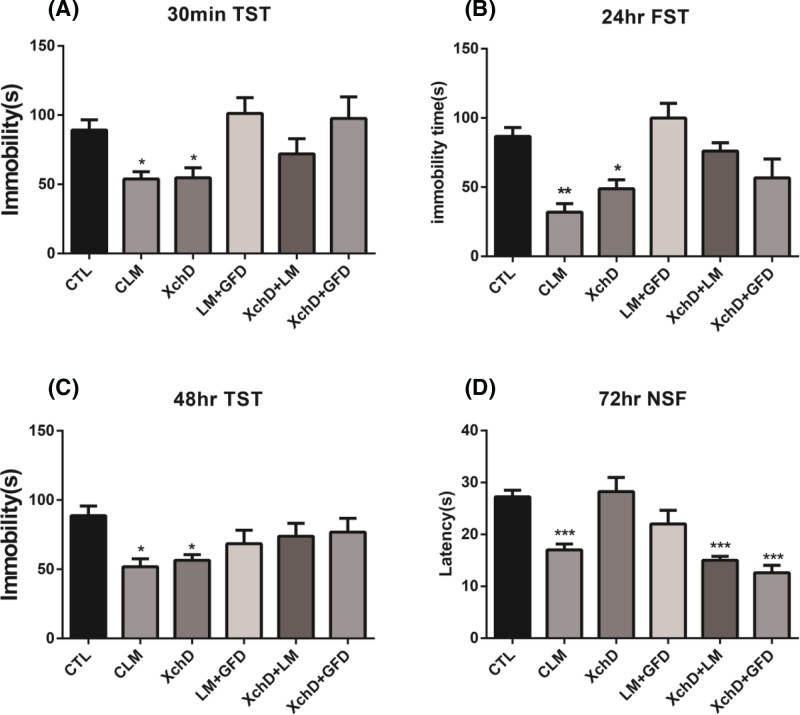
Figure 5. XchD was primarily responsible for rapid antidepressant-like effect of CLM.
Mice were grouped into CTL, CLM, XchD, LM+GFD, XchD+LM, XchD+GFD. (A,C) TST was carried out at 30 min and 48 hr after drug administration. (B) FST was carried out at 24 hr after drug administration. Immobility time was measured for the last 4 min during the 6-min testing time in both TST and FST. Compared with control group, a single administration of both CLM and XchD reduced the immobility time in TST at 30 min and 48 hr. By 24 hr, CLM and XchD significantly reduced the immobility time in FST. (D) NSF test was carried out at 72 hr after drug administration. The time of latency to feed was measured during 10-min test after a single administration. XchD did not reduce the latency to feed in NSF, whereas both XchD+LM and XchD+GFD, similar to CLM significantly reduced the latency to feed. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001 compared with control. Statistical evaluation was performed using multiple comparisons made using one-way ANOVA, followed by the Newman–Keuls multiple range test, and a value of P<0.05 was considered statistically significant. Data represent mean ± S.E.M. and n=6–8/group.