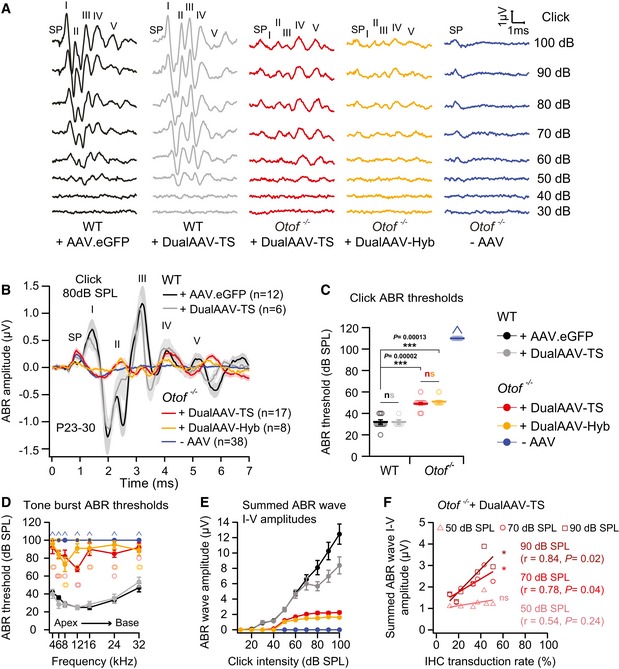
-
A
Representative ABR wave traces in response to broadband click sound stimuli from otoferlin dual‐AAV‐TS (P26) and dual‐AAV‐Hyb (P27)‐injected CD1B6F1‐Otof
−/− animals. AAV2/6.eGFP (+AAV.eGFP; P28) and dual‐AAV‐TS (P27)‐injected CD1B6F1 wild‐type, and non‐injected control Otof
−/− littermate (‐AAV; P26) mice served as controls. SP: summating potential; ABR waves are indicated from I‐V.
-
B
Average ABRs evoked by 80 dB SPL click sound stimuli for 20 clicks/s.
-
C, D
ABR click sound (C) and tone burst (D) thresholds in otoferlin dual‐AAV‐treated Otof
−/− mice compared to wild‐type and non‐treated Otof
−/− control animals. In (D), the two best animals are depicted with open circles. Animals with thresholds exceeding the maximum loudspeaker output (arrows) of 100 dB SPL for clicks and 90 dB SPL for tone bursts were set to 110 dB SPL and 100 dB SPL, respectively. Apical and basal cochlear turns are indicated as Apex and Base, respectively.
-
E
Summed ABR wave I‐V amplitudes at different click sound intensities in otoferlin dual‐AAV‐injected, non‐injected Otof
−/−, and wild‐type control mice.
-
F
Summed ABR wave I‐V amplitudes of individual dual‐AAV‐TS‐treated CD1B6F1‐
Otof
−/− animals (
n = 8 animals; from Fig
3E) plotted against their full‐length otoferlin IHC transduction rates (from Fig
1D, C‐term otoferlin).
r: correlation coefficient.
Data information: In (B–F), age of analyzed animals: P23–30. In (B, C, E), number of analyzed mice: CD1B6F1 wild‐type animals (+AAV.eGFP:
n = 12 mice, dualAAV‐TS:
n = 6 mice) and CD1B6F1‐
Otof
−/− animals (dualAAV‐TS:
n = 17 mice, dualAAV‐Hyb:
n = 8 mice, ‐AAV:
n = 38 mice). In (D), number of analyzed mice is the same as for (B, C, E) except: CD1B6F1‐
Otof
−/− animals (dualAAV‐TS:
n = 16 mice). In (B–E), data are represented as mean ± s.e.m. In (C, D, F), individual animals are depicted with open symbols. In (F),
r ≥ 0.5 positive correlation (70 dB SPL and 90 dB SPL: Pearson correlation test; 50 dB SPL: Spearman correlation test). In (C), ns
P > 0.05; *
P ≤ 0.05; ***
P ≤ 0.001 (Kruskal–Wallis test followed by Dunn's multiple comparison test).