Figure 2.
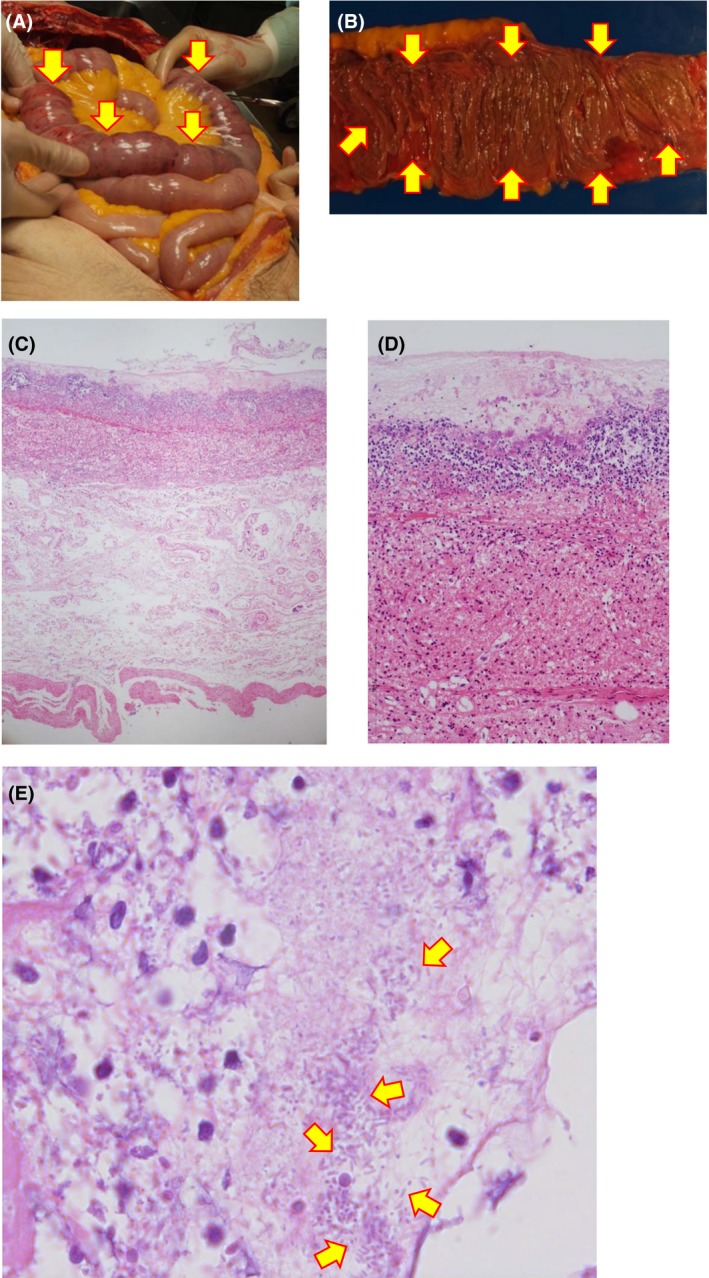
Autopsy findings in a 79‐year‐old man with fulminant pseudomembranous enterocolitis caused by Klebsiella oxytoca. A, Images of intestinal necrosis in the autopsy. Mucosal necrosis is observed between the duodenum and jejunum (arrows). B, Intestinal necrosis is observed between the duodenum and jejunum. Arrows indicate pseudomembrane formation. C, Microscopic view. Hematoxylin–eosin staining (×40). D, High‐power view (×100) of (C). Hematoxylin–eosin staining reveals mucosal hemorrhagic necrosis and submucosal edema in conjunction with pseudomembranous formation. E, Maximum‐power view (×1,000) of (C). Arrows indicate gram‐negative bacilli that correspond to K. oxytoca.
