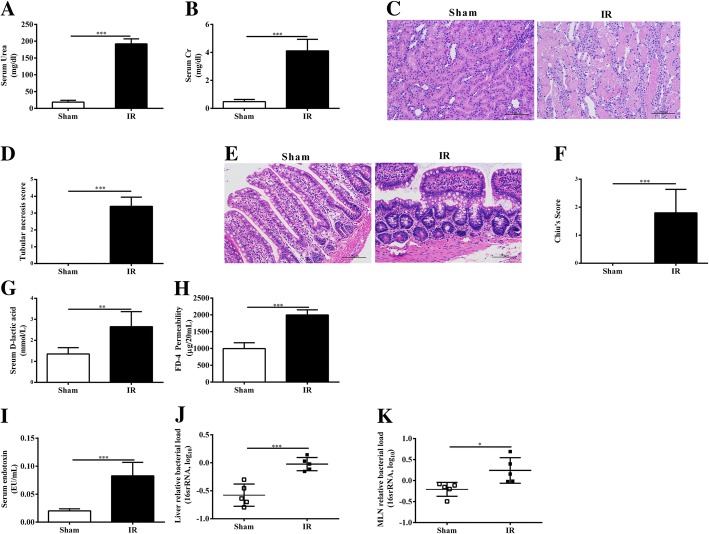
Fig. 1.
The intestinal consequences of renal IR induced AKI. Renal function was evaluated by serum urea (a) and creatinine (b) levels. Kidney and ileum morphological alterations were evaluated by HE stained sections (original magnification× 200) and scored (c-f). Intestinal permeability was evaluated by serum D-lactic (g) and an ex vivo isolated sac method (h). The level of serum endotoxin was measured using a Kinetic Turbidimetric LAL method (i). Bacterial load was measured at liver (j) and mesenteric lymph nodes (k). Bacterial load was represented by relative bacterial load in log as quantified by qPCR of 16S primer targets normalized to β-actin. Higher values represent more bacteria. Data are expressed by mean ± SD. The two-tailed unpaired t test was used (n = 5 per group). *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001