Fig. 2.
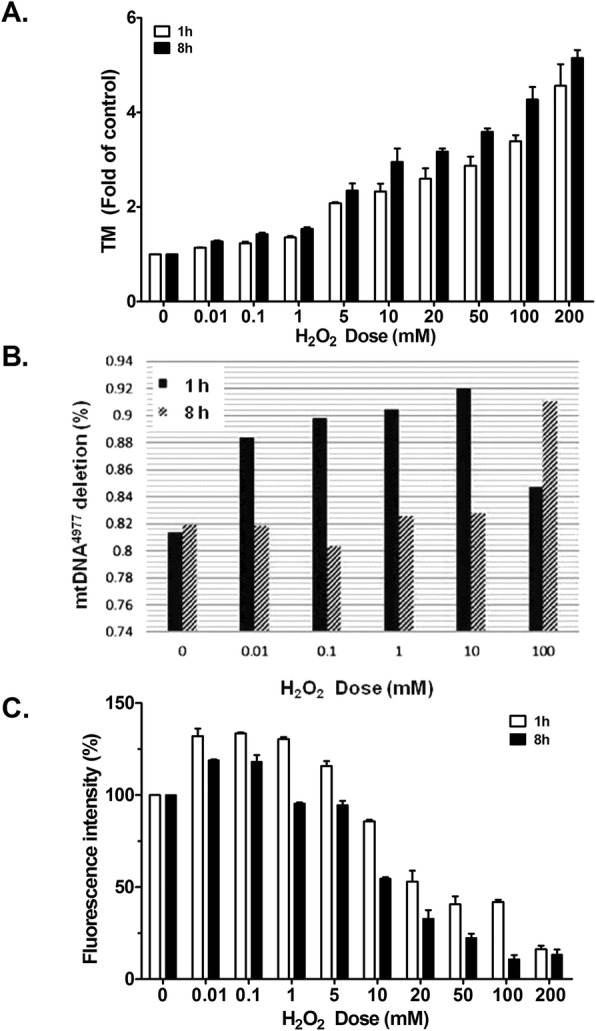
DNA damage and glutathione (GSH) levels increased after the NHOKs had been exposed to H2O2. (a) A comet assay was used to analyze the nDNA damage caused by H2O2-induced oxidative attacks on NHOK DNA. The cells were exposed to H2O2 for 1 h or 8 h. Data are shown in folds, by comparing the changes to the control at 0 mM (set as 1). The experiment was repeated 3 times, and the values are expressed as mean (± SD). (b) qPCR was used to measure mtDNA4977 deletion for each dose after NHOKs had been exposed to H2O2 for 1 h and 8 h. The experiment was repeated 4 times and the values are expressed as mean (± SD). (c) The quantity of intracellular GSH was determined by measuring the CMF that remained in the NHOKs. Data are expressed as a % of fluorescence intensity. The untreated cell culture was the negative control (set as 100%). The experiment was repeated 3 times, and values are expressed as mean (± SD)
