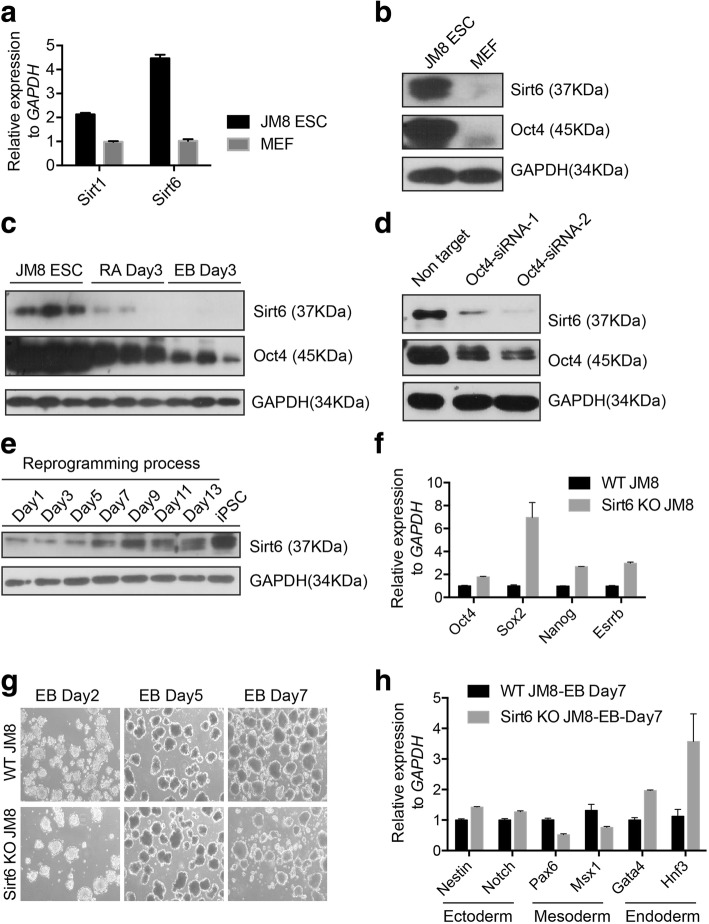
Fig. 1.
Sirt6 is highly expressed in pluripotent cells relative to differentiated somatic cells. a Relative mRNA expression level of Sirt1and Sirt6 in JM8 ESC and MEFs. Data were normalized to the expression levels in MEFs; GAPDH was regarded as internal control gene. Data represent means ± SD of three independent experiments. b Western blotting analysis of Sirt6 showed that Sirt6 protein level was much higher in ESCs than in MEFs. c Western blotting analysis showed that protein expression of Sirt6 was significantly decreased at day 3 in RA-induced ES differentiation or EB differentiation system. d Western blotting analysis of Sirt6 showed that Sirt6 protein level was downregulated in ESCs after RNAi of Oct4. Two siRNA of different sequences (SiOCT4-1 and SiOCT4-2) efficiently knockdown Oct4 expression at protein level. GAPDH was used as the internal control. e Western blotting analysis of Sirt6 was shown in different time points (day 1/3/5/7/9/11/13) after MEFs were induced by OSKM factors and also final reprogrammed iPS cell lines. f Pluripotency genes (Oct4, Sox2, Nanog, Esrrb) in Sirt6 knockout (KO) ES cells (Additional file 2: Figure S2B and C) were analyzed compared to wild-type iPSCs by qRT-PCR. Data were normalized to the expression levels in wild-type control. Data represented as mean ± SD from three independent assays. g EB formation of different time points in Sirt6 KO ES cells compared to wild-type control. h Three germ layer marker genes (Nestin and Notch for ectoderm; Pax6 and Msx1 for mesoderm; Gata4 and Hnf3 for endoderm) in Sirt6 KO ES cells were analyzed compared to wild-type control by qRT-PCR during EB formation at day 7. Data represented as mean ± SD from three independent assays