Figure 1. The T box mechanism.
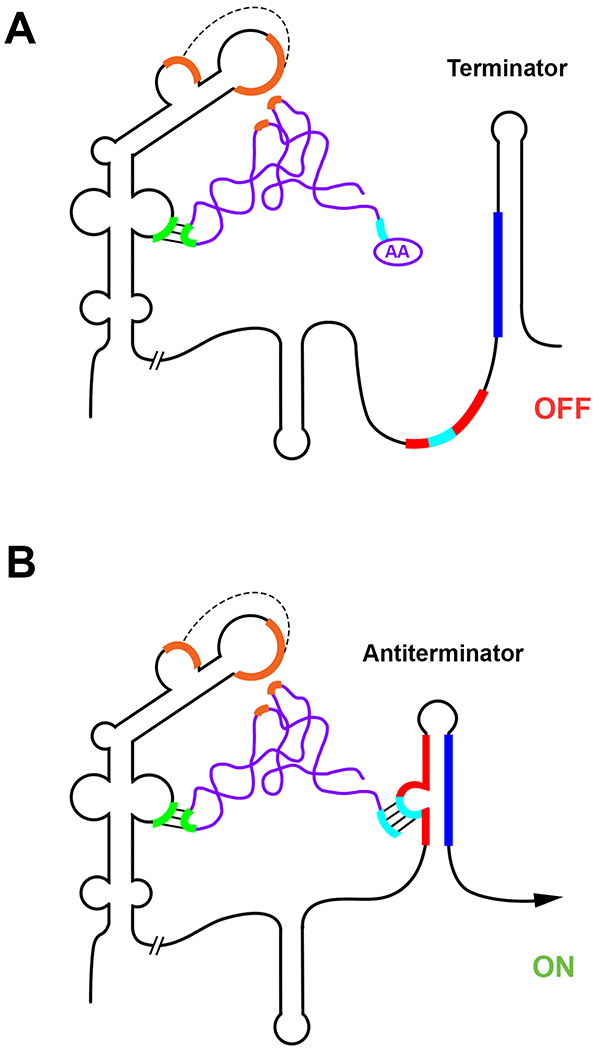
A. tRNA interacts with Stem I of the T box leader RNA at two locations. The tRNA anticodon base pairs with the Specifier Sequence (green), and the tRNA elbow stacks with the Stem I platform (orange), which is formed by interactions between conserved sequence motifs. The presence of an amino acid (AA) at the 3’ end of a charged tRNA blocks the base-pairing interaction with a bulge in the antiterminator helix. The terminator helix forms and transcription terminates, which turns gene expression off. B. Uncharged tRNA also interacts with the Specifier Sequence and Stem I platform, and the acceptor arm base pairs with a bulge in the antiterminator helix (cyan). The stabilization of the antiterminator prevents formation of the competing terminator helix, and RNA polymerase continues to transcribe the downstream coding sequence.
