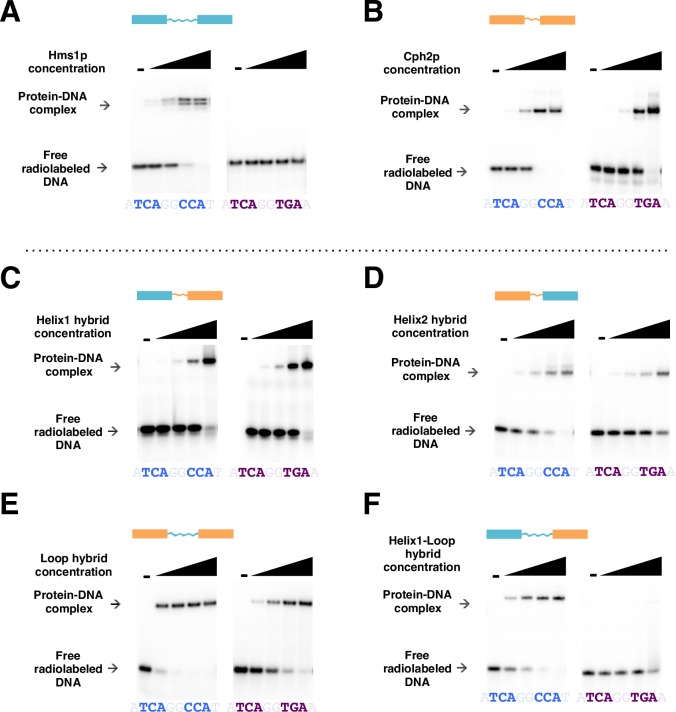
Fig 5. DNA binding specificity in the C. albicans SREBP Hms1 is conferred by residues in the first helix and loop region of its DNA binding domain.
(A-F) Gel shift assays to determine the protein regions of the C. albicans SREBP Hms1p (cyan) that are necessary to discriminate between binding to its cognate DNA binding site (sequence in blue) and binding to the canonical E-box sequence (purple) typically recognized by other SREBPs. Chimeric proteins were generated by exchanging parts of the DNA binding domain of CaHms1p (cyan) with that of CaCph2p (orange). The latter protein shows much reduced ability to discriminate in vitro between both DNA binding sites (B). Chimeric proteins harboring the CaHms1p first helix (C), second helix (D) or loop (E) alone displayed no discrimination between the two sequences. The chimeric protein containing the CaHms1p first helix and loop bound preferentially to the Hms1p’s cognate DNA binding sequence (F). The protein concentrations evaluated in the gel shifts were 0, 1.56, 6.25, 25 and 100 nM.