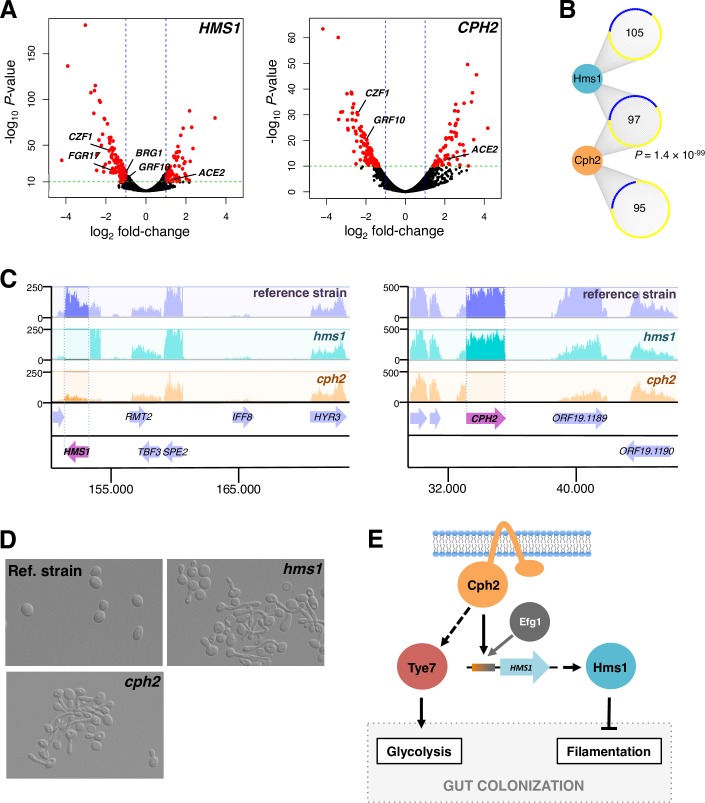
Fig 7. C. albicans Hms1p and Cph2p form a regulatory cascade that controls a morphological switch under anaerobic conditions.
(A) Identification of transcripts regulated by HMS1 and CPH2. Total RNA was prepared from wild-type, hms1 and cph2 deletion mutant strains grown at 37°C under anaerobic conditions. Shown are volcano plots where each dot represents one transcript. In red are significantly up- or down-regulated transcripts. The regulators of filamentation ACE2, BRG1, CZF1, FGR17 and GRF10 are marked. (B) Overlap of targets of regulation between Hms1p and Cph2p. Up-regulated genes are shown in yellow and down-regulated genes in blue. The hypergeometric distribution was employed to calculate the significance of the overlap. (C) Representative segments of RNA-Seq track for the wild-type reference strain (purple), hms1 (blue track) and cph2 (orange track) mutants. Notice that the levels of the HMS1 transcript are dramatically reduced in the cph2 deletion strain (left panel). (D) HMS1 and CPH2 prevent C. albicans filamentation under anaerobic conditions. The wild-type reference strain, cph2 and hms1 mutants were grown in Todd-Hewitt broth at 37°C under anaerobiosis for 24 h. Morphology of cells was examined by microscopy. (E) Model depicting the relationships among the three C. albicans SREBPs.