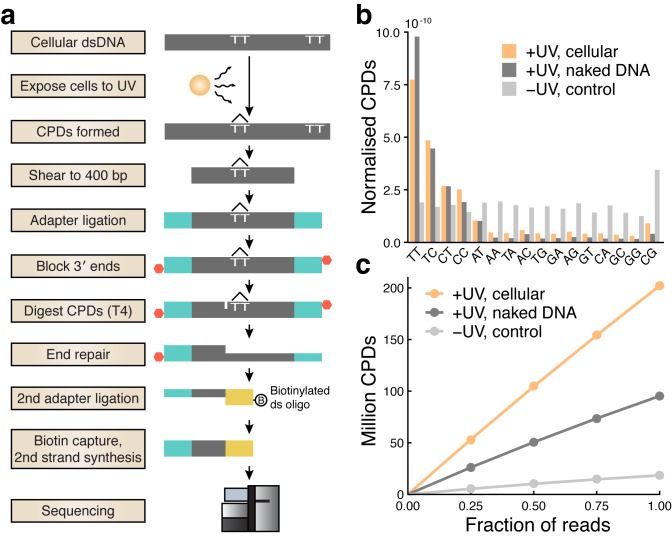
Fig 3. High-coverage mapping of UV-induced cyclobutane pyrimidine dimers across the human genome.
(a) Schematic of the experimental protocol. (b) Distribution of dinucleotides at which CPDs were detected, showing an expected preference for dipyrimidines. Counts from cellular, naked (acellular) and no-UV-control samples were normalized with respect to genomic dinucleotide counts as well as sequencing depth. (c) The number of detected CPDs in each library following removal of PCR duplicates shown at full depth, as well as based on subsampled data (25, 50 and 75%) to simulate lower sequencing depth.