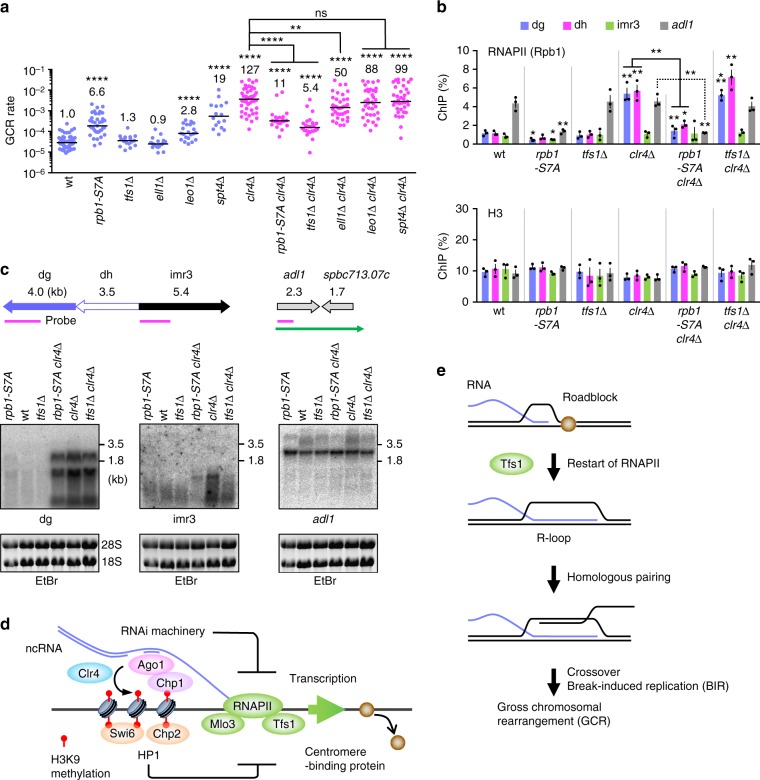
Fig. 7.
Clr4 suppresses centromeric gross chromosomal rearrangements (GCRs) by repressing transcription that is dependent on RNAPII CTD Ser7 and Tfs1/TFIIS. a GCR rates of wild-type, rpb1-S7A, tfs1∆, ell1∆, leo1∆, spt4∆, clr4∆, rpb1-S7A clr4∆, tfs1∆ clr4∆, ell1∆ clr4∆, leo1∆ clr4∆, and spt4∆ clr4∆ strains (TNF5676, 6848, 6688, 7042, 7130, 7055, 5702, 6850, 6726, 7063, 7154, and 7057, respectively). The two-tailed Mann-Whitney test. **P < 0.01, ****P < 0.0001; ns, not significant. b Chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) analysis of RNAPII (Rpb1) and H3 in wild-type, rpb1-S7A, tfs1∆, clr4∆, rpb1-S7A clr4∆, and tfs1∆ clr4∆ strains (TNF5921, 6862, 6722, 5948, 6864, and 6799, respectively). The two-tailed Student’s t-test. *P < 0.05, ***P < 0.001. c Northern blotting using total RNAs prepared from log phase cultures of rpb1-S7A, wild-type, tfs1∆, rpb1-S7A clr4∆, clr4∆, and tfs1∆ clr4∆ strains. Illustrated are the positions of DNA probes used in Northern blotting (magenta bars) and the readthrough transcript of adl1 (a green arrow). RNAs were separated by 1.0% agarose gel under denatured condition, stained with ethidium bromide (EtBr) (the bottom panel), transferred onto a nylon membrane, and hybridized with specific probes (the top panel). Uncropped images of depicted gels and blots are shown in Supplementary Fig. 12. d A model that explains how heterochromatin suppresses GCRs at centromeres. With the aid of the RNAi system, Clr4 catalyzes H3K9 methylation at centromeres. H3K9 methylation marks are recognized by the chromodomain proteins including Clr4, Swi6, Chp2, and Chp1. Both HP1 homologs, Swi6 and Chp2, and an RNAi component Chp1 are required for full suppression of GCRs. In addition to the Clr4 recruitment, RNAi machinery may prevent transcription of noncoding RNAs from centromere repeats to suppress GCRs. RNAPII transcription that depends on CTD Ser7, Mlo3, and Tfs1/TFIIS causes centromeric GCRs possibly by removing DNA binding proteins, such as replication factors, from DNA. e Tfs1/TFIIS-dependent transcription might remove the roadblock that binds to DNA and produce R-loops, which facilitate interaction between centromere repeats at non-allelic positions and cause crossover and/or break-induced replication (BIR) that leads to GCRs