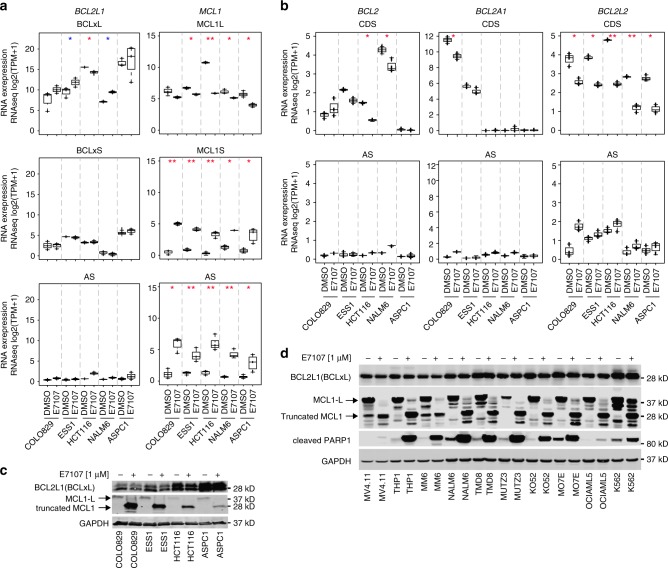
Fig. 3.
Antiapoptotic BCL2 family genes exhibit differential sensitivity to E7107-induced splicing modulation. a RNA-seq analysis of BCL2L1 and MCL1 upon E7107 treatment (at GI50) in cancer cell lines COLO829 (35 nM for 6 h), ESS1 (16 nM for 6 h), HCT116 (50 nM for 6 h), NALM6 (15 nM for 6 h), and ASPC1 (41 nM for 6 h). RNA expression levels represent RNA reads for corresponding coding sequence (CDS) of the functional protein isoforms (L antiapoptotic long form, S proapoptotic short form) or aberrant splicing (AS) events that are not predicted to encode functional proteins. b RNA-seq analysis of BCL2, BCL2A1, and BCL2L2 under same conditions shown in a. *p < 0.01, **p < 0.001; red asterisks: proapoptotic events with median expression log2(TPM + 1) > 2, blue asterisks: antiapoptotic events with median expression log2(TPM + 1) > 2. c Western blot analysis of BCLxL and MCL1 protein expression upon treatment with E7107 (1 μM for 6 h). GAPDH was used as the loading control. d Western blot analysis of BCLxL, MCL1, and cleaved PARP1 protein expression in a panel of leukemia cell lines upon treatment with E7107 (1 μM for 6 h). GAPDH was used as the loading control