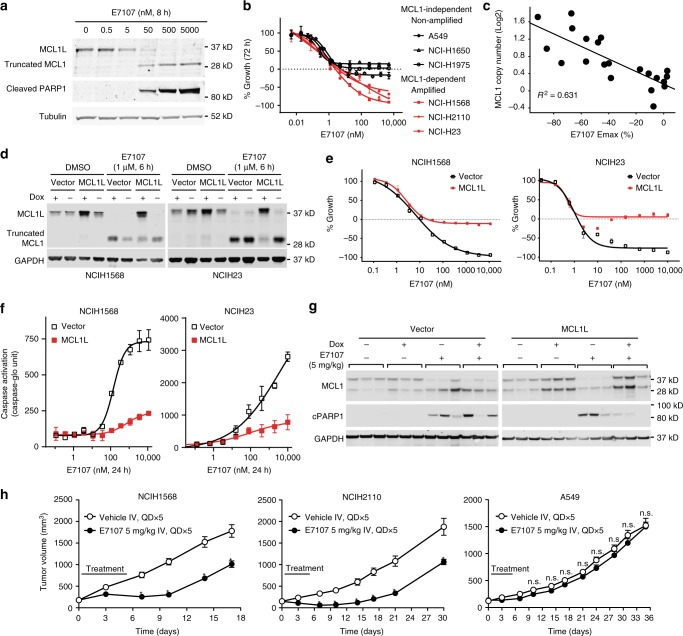
Fig. 5.
E7107 induces MCL1-dependent apoptosis in MCL1-overexpressed/dependent NSCLC cells. a Western blot analysis of MCL1 protein and cleaved PARP1 as an indicator as apoptosis. Tubulin was used as loading control. NCIH1568 cells were treated with E7107 as indicated. b Growth curves measured by CellTiter-Glo (CTG) in NSCLC cell lines. Data represent means ± SD of biological triplicates. c Correlation of MCL1 copy number and E7107 Emax in 21 NSCLC cell lines. d Western blot analysis of MCL1 and GAPDH (loading control) protein expression in NSCLC cell lines transduced with vector control (Vector) or Dox-inducible expression of MCL1L cDNA (MCL1L). Cells were treated with DMSO or E7107 as indicated. e Growth curves measured by CellTiter-Glo (CTG); and f Caspase activation detected by Essen Biosciences IncuCyte Caspase-3/7 Green Apoptosis Assay. Data represent means ± SD of biological triplicates. NSCLC cell lines transduced with vector control (Vector) or Dox-inducible expression of MCL1L cDNA (MCL1L) in the presence of 300 ng ml−1 Dox. Cells were treated with E7107 as indicated. g Western blot analysis of NCIH1568 xenograft tumor samples. The engineered cell lines from d were used for the in vivo studies. h Tumor growth curves measured by tumor volume of three NSCLC xenograft models treated with vehicle or E7107. H1568: 8 mice/group; H2110: 6 mice/group; A549: 8 mice/group. Statistical significance was analyzed by the Holm–Sidak method in Prism. Each row was analyzed individually, without assuming a consistent SD. *p < 0.001; n.s. not significant, p > 0.1