Fig. 5.
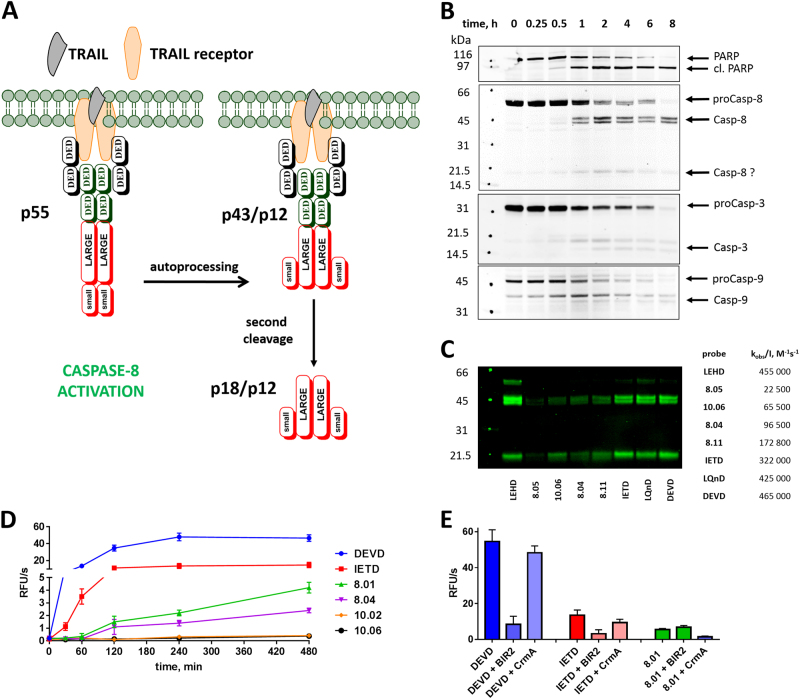
Use of small-molecule substrates and ABPs reveals caspase activation in TRAIL-stimulated Jurkat T cells. a The general scheme of caspase-8 activation upon TRAIL stimulation. Procaspase-8 (p55) is activated by dimerization at the DISC and undergoes auto-processing within the catalytic domain to generate p43/p12 fragments, which are further cleaved by the release of the DEDD recruitment domain into p18/p12 subunits [65] Jurkat T cells primarily express caspase-8 isoforms a and b, which differ by a short indel in the DED domain region, hence, the doublets seen in the 55 kDa and 43 kDa regions [66, 67] (of b,c) . b Western blots with specific antisera demonstrating the kinetics of caspase and PARP processing after TRAIL stimulation. The band around 20 kDa in the caspase-8 blot may be the p18 (large) subunit or a nonspecific band. c Cells were preincubated with indicated ABPs for 2 h and stimulated for 8 h with TRAIL. Cell lysates were then prepared and treated with streptavidin resin, the resin was washed, and the captured proteins were then eluted in boiling SDS buffer and run on SDS-PAGE for immunoblotting with caspase-8 antiserum. d Caspase activity in Jurkat cells at various time points after apoptosis induction and using indicated broad-spectrum and selective ACC substrates. e Caspase activity measured in Jurkat T cells at 8 h after apoptosis induction in the presence or absence of caspase inhibitors XBIR2 (1 µM; for caspase-3/-7) and CrmA (1 µM; for caspase-8). RFU relative fluorescence units. Western blots from b,c were performed twice, and the kinetic experiments in d,e were performed three times. Average values (with SD) are presented